A Field Guide to Querying and Report Computations with SPL
Preface
Query and reporting applications often involve complex computations. Since data is typically stored in databases, these computations are usually implemented using SQL. However, SQL has multiple disadvantages, such as incomplete set-orientation, lack of inherent ordering, difficulty in performing step-by-step computations, and debugging challenges, which often lead to cumbersome or even unwritable code. As a result, various difficulties arise frequently. A clear example of this is the globally renowned IT Q&A website stackoverflow.com,where people post questions almost every day seeking solutions to challenging SQL problems.
In contrast, esProc SPL (Structured Process Language) achieves more thorough set-orientation, features inherent ordering, supports step-wise computations, eases debugging, and simplifies coding, significantly reducing computational complexity.
SPL can be embedded into applications, connect to databases to read data, and then perform complex computations. This process only requires very simple SQL for data retrieval, thus avoiding difficult to write SQL.
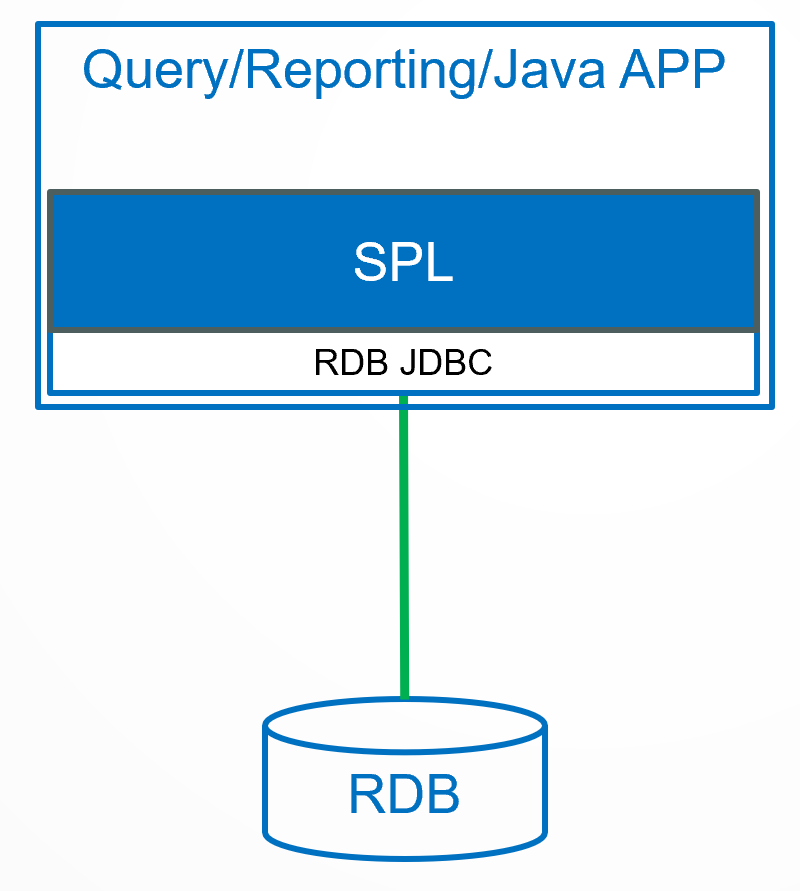
This article, targeting various complex computational tasks, explains SPL’s problem-solving methods in separate chapters, including: retaining grouped subsets, order-based computations, relative position reference, order-based grouping, dynamic row-to-column/column-to-row transposition, and so on.
The article is accompanied by a number of txt files, three of which – Orders, Employee and Client, serve as public datasets for most of the examples. Their data structures are as follows:
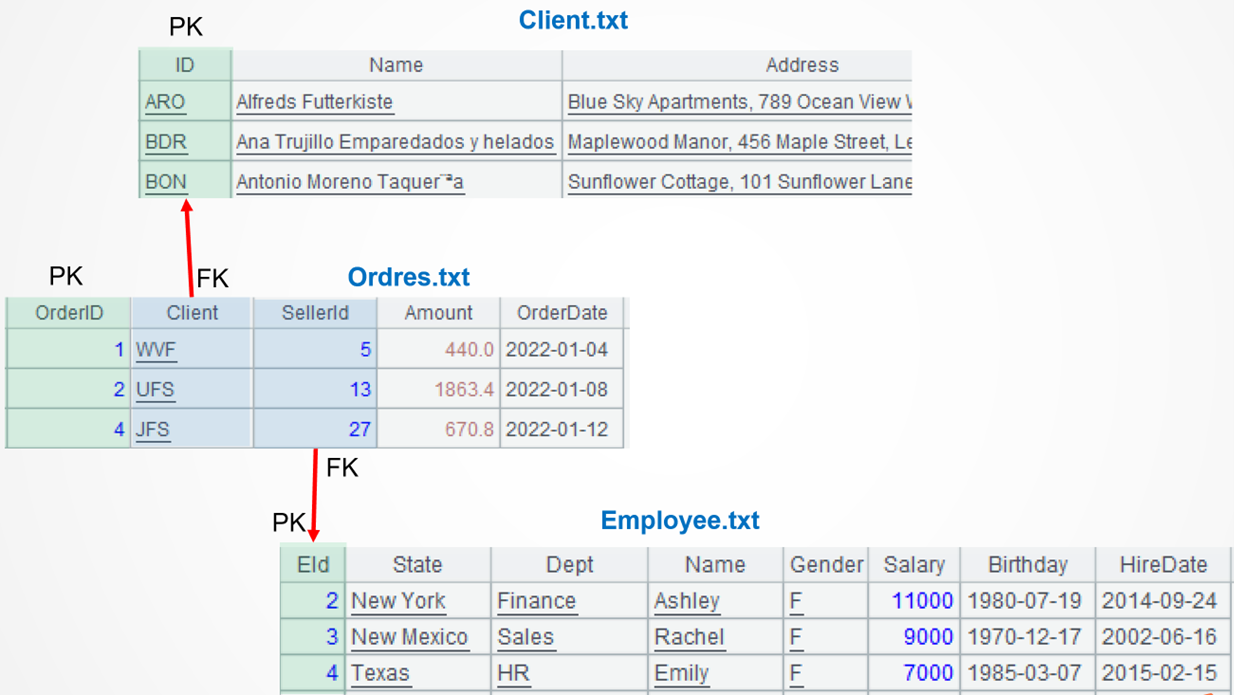
The special datasets some examples need will be specifically provided when used.
Table of contents
Preparation
Basic regular operations
1 Computing and processing grouped subsets
2 Order- and position-based operations
3 Order-based neighboring member referenc
4 Order-based grouping
5 Align and group data by members of an external set
6 Multilevel join operations
7 Row-to-column/column-to-row transposition
8 Multilevel JSON computations
9 Post-grouping set operations
10 Order-based computations on sets of strings
11 Datetime sequence computations
12 Expand to multiple records based on the specified rule
SPL Official Website 👉 https://www.esproc.com
SPL Feedback and Help 👉 https://www.reddit.com/r/esProcSPL
SPL Learning Material 👉 https://c.esproc.com
SPL Source Code and Package 👉 https://github.com/SPLWare/esProc
Discord 👉 https://discord.gg/sxd59A8F2W
Youtube 👉 https://www.youtube.com/@esProc_SPL



Chinese: https://c.raqsoft.com.cn/article/1752483977188