A Field Guide to Querying and Report Computations with SPL - 4 Order-based grouping
4. Order-based grouping
Unlike simple equi-grouping operations, order-based grouping operations groups members by comparing neighboring ones or checking whether a member meets the specified condition or not while preserving the original order. SQL does not support order-based grouping, so it typically turns to a workaround such as flagging to achieve this indirectly, generating complex code. When the order-based grouping involves maintaining grouped subsets, the code becomes even more complex.
Example 1: Find the start and end of months when salespeople who consistently ranked monthly first
Source data: Each salesperson’s sales amount per month per year.
Target: Find record of the salesperson boasting the highest sales amount in each month, sort records by month, and put the neighboring ones in the same group if they have the same sellerId value, and get the month in the first record and that in the last record from each group.
SPL code:A |
|
1 |
$select year(OrderDate)*100+month(OrderDate) YM,SellerId,sum(Amount) SubTotal from 4\Orders41.txt group by year(OrderDate)*100+month(OrderDate),SellerId |
2 |
=A1.group(YM).(~.maxp(SubTotal)) |
3 |
=A2.group@o(SellerId) |
4 |
=A3.new(SellerId,~.count():cnt,~.YM:begin,~.m(-1).YM:end) |
5 |
=A4.select(cnt>1) |
A1: Load data, during which each salesperson’s sales amount per month per year is computed in SQL.
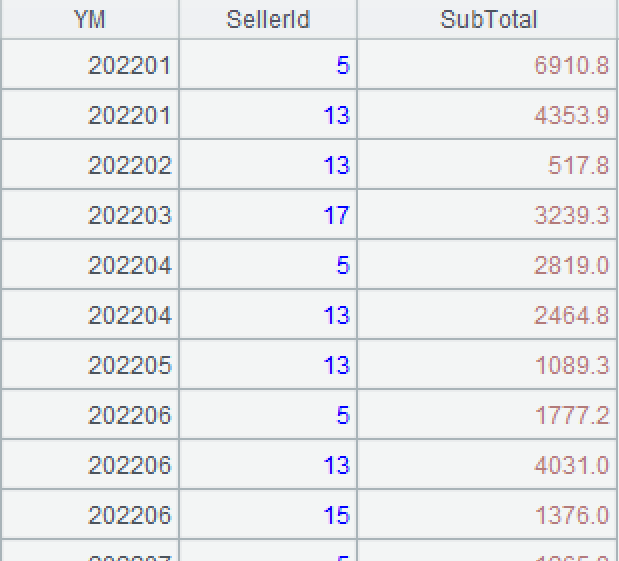
A2: Group A1’s records by yearmonth without aggregation and retrieve the record having the largest sales amount from each grouped subset. The maxp() function searches for the record that makes the expression have the greatest value.
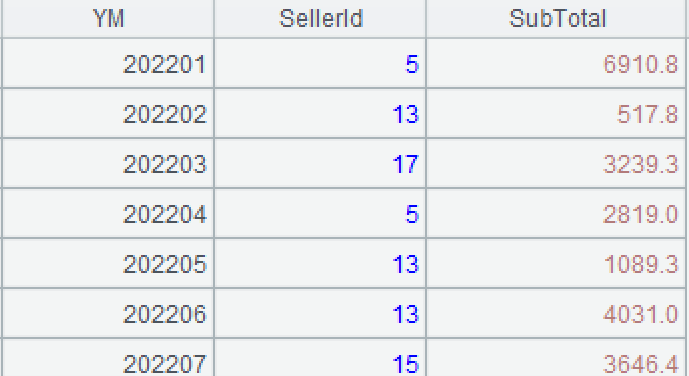
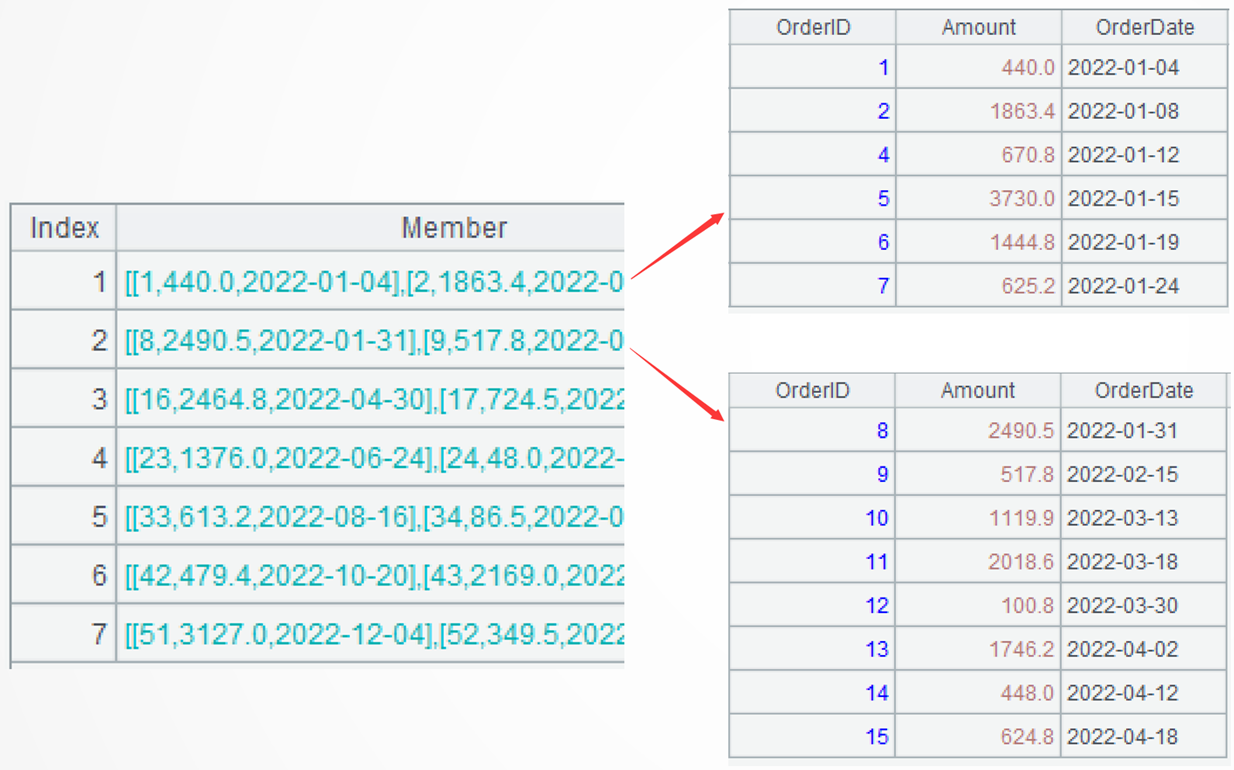
A3: Put records of same salesperson in one group without aggregation. Each group consists of a set. The group@o(SellerId) function puts neighboring order records of same salesperson to the same group.
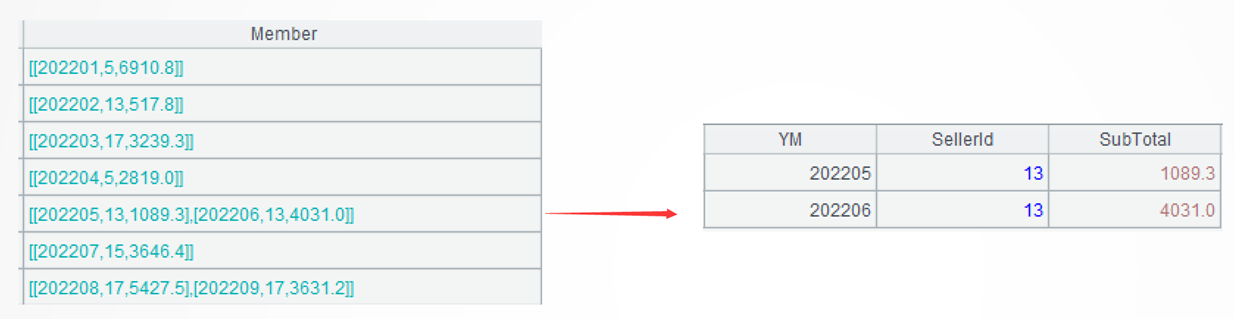
Learning point: Grouping by comparing neighboring members
In SPL, both groups()function and group() function can work with @o option to put neighboring records having the same specified field value to the same group.
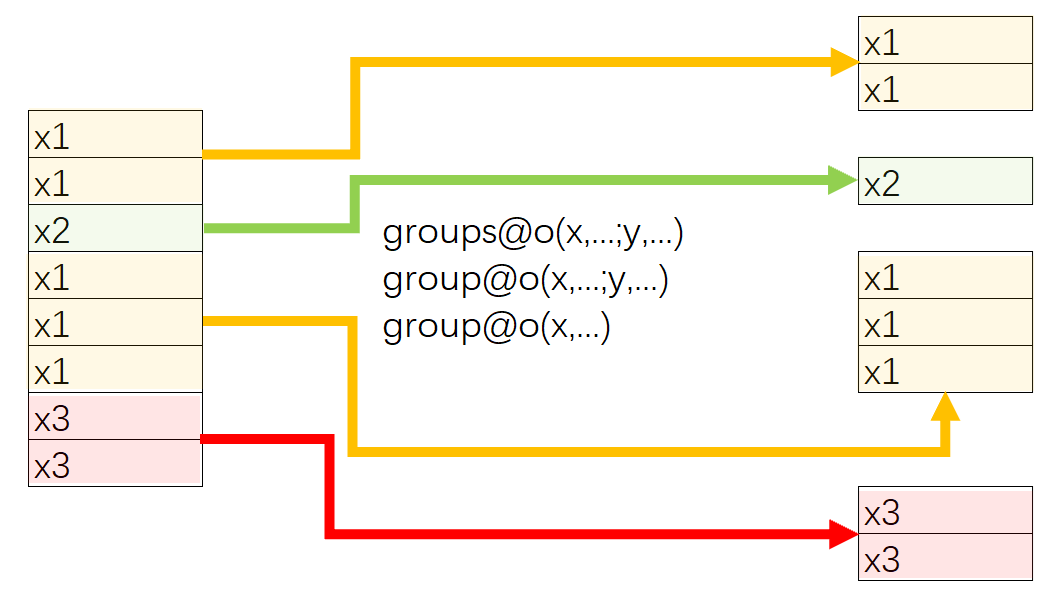
Parameter x: One or multiple grouping expressions.
Parameter y: One or multiple aggregate expressions.
A4: Create a new table sequence based on A3 by generating one record for each group. Fields of one record include salesperson, intra-group record count, month of the current group’s first record, and month of the current group’s last record. ~ represents the current group; ~.m(1) means the first record of the current group, which can be abbreviated as ~1 or ~. ~.m(-1) denotes the last the record of the current group, which cannot be abbreviated.
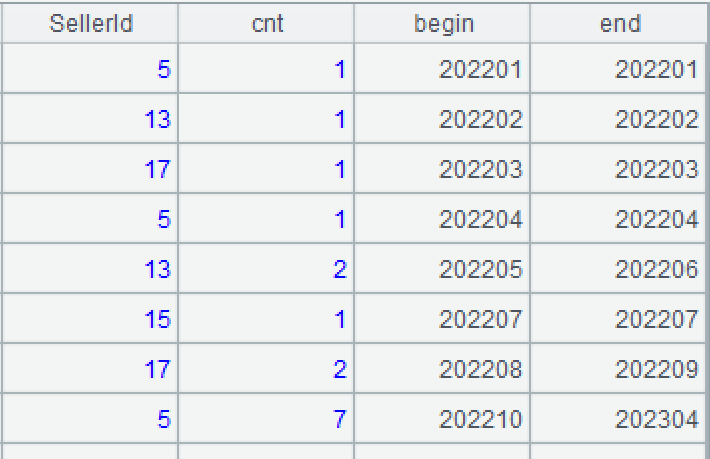
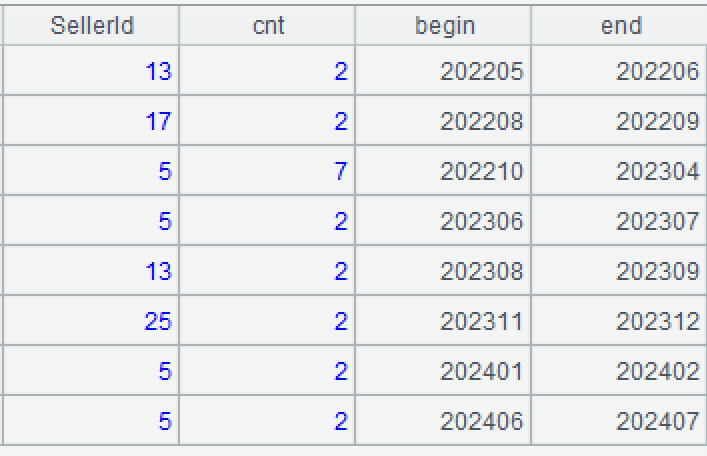
A5: Select groups having at least two records.
Example 2: Find the largest count of months when sales consecutively rise
Source data: Order amounts per month per year.
Targe: Put continuous months when sales rise consecutively to the same group, and find the largest count of records in a group. In other words, you create a new group whenever the sales decrease compared with the preceding month.
SPL code:
A |
|
1 |
$select year(OrderDate) year, month(OrderDate) month,sum(Amount) subTotal from Orders.txt group by year(OrderDate) , month(OrderDate) |
2 |
=A1.group@i(subTotal<=subTotal[-1]) |
3 |
=A2.max(~.len()) |
A1: Load data.
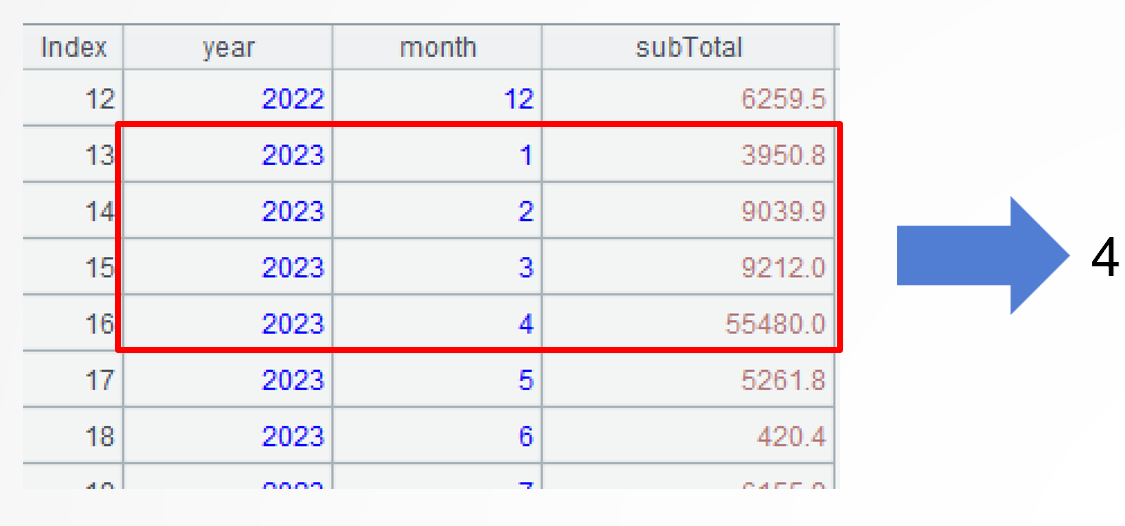
A2: Create a new group when sales amount of the current month is smaller than that in the preceding month. This amounts to putting consecutively rising months in the same group, which consists of a set. The group@i() function is used to perform conditional grouping.
Learning point: Conditional grouping
SPL’s groups()function and group() function work with @i option to perform conditional grouping on ordered data.
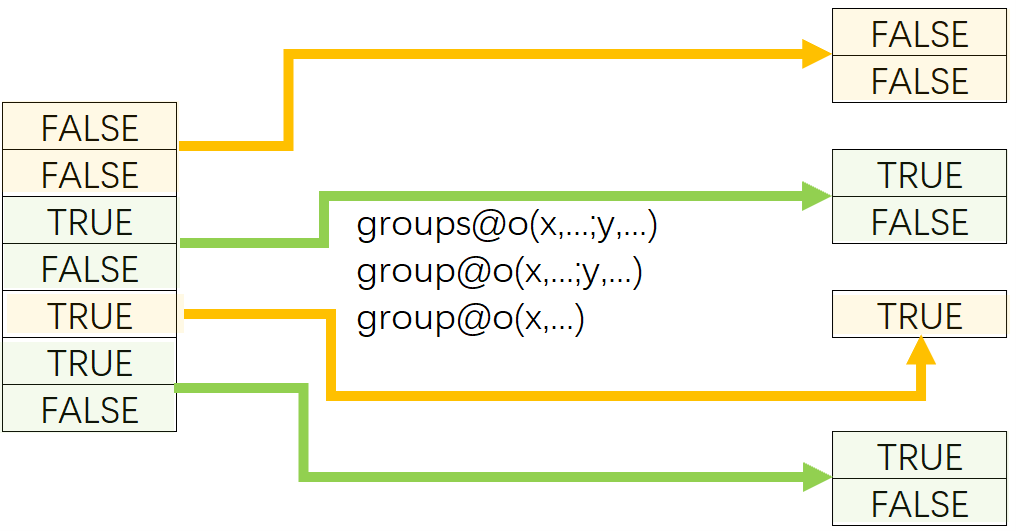
Parameter x: One or multiple conditional grouping expressions. Create a new group when the condition is met.
Parameter y: One or multiple aggregate expressions.
In addition, @o option is in essence the @i option with a simple condition, which creates a new group when the current member is different from the last one.
A3: Count members in each group and return the largest count.
Example 3: Compute the amount in a bonus pool that is established again whenever the cumulative amount reaches $10000
Source data: Orders data of the year 2022.
Target: Accumulate order amounts in the chronological order. Each time the cumulative amount reaches a maximum of $10,000, establish a bonus pool where the bonus amount is 10% of the cumulative value (the bonus will be distributed to salespeople corresponding to these orders). Now, number the bonus pools sequentially and compute the amount in each bonus pool and get the list of corresponding order numbers. Note that when the cumulative amount exceeds $10000, the current order should be treated as the first order of the next bonus pool.
SPL code:
A |
|
1 |
$select OrderID,Amount,OrderDate from Orders.txt where year(OrderDate)=2022 order by OrderDate |
2 |
>cum=0 |
3 |
=A1.group@i(if( (cum+=Amount)>10000, cum=Amount, null)) |
4 |
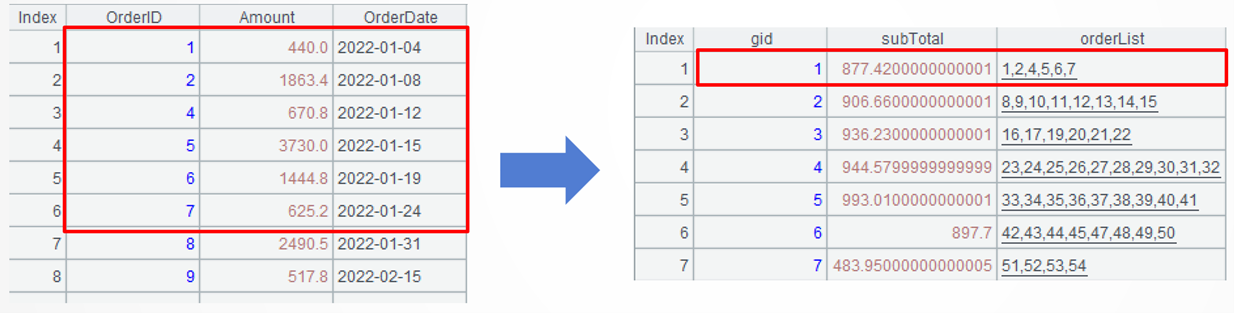
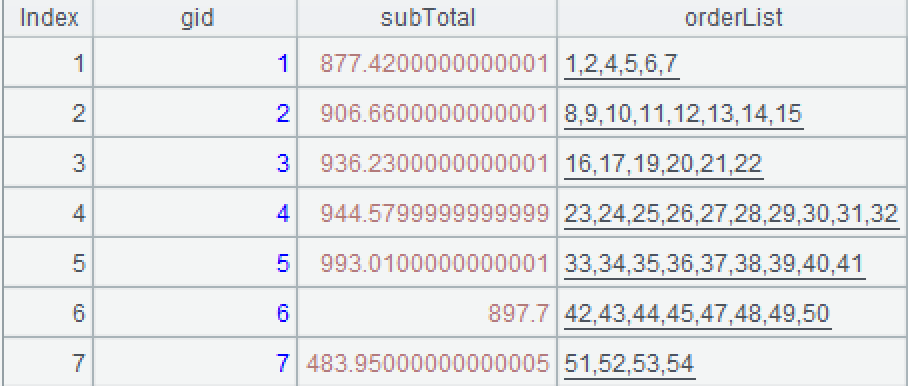
=A3.new(#:gid,~.sum(Amount)*0.1:subTotal,~.(OrderID).concat@c():orderList) |
A1: Load data.
A2: Set the initial value for the cumulative value or bonus pool.
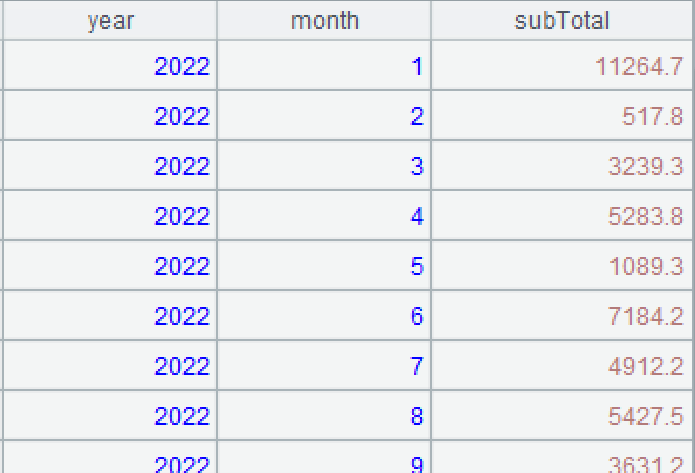
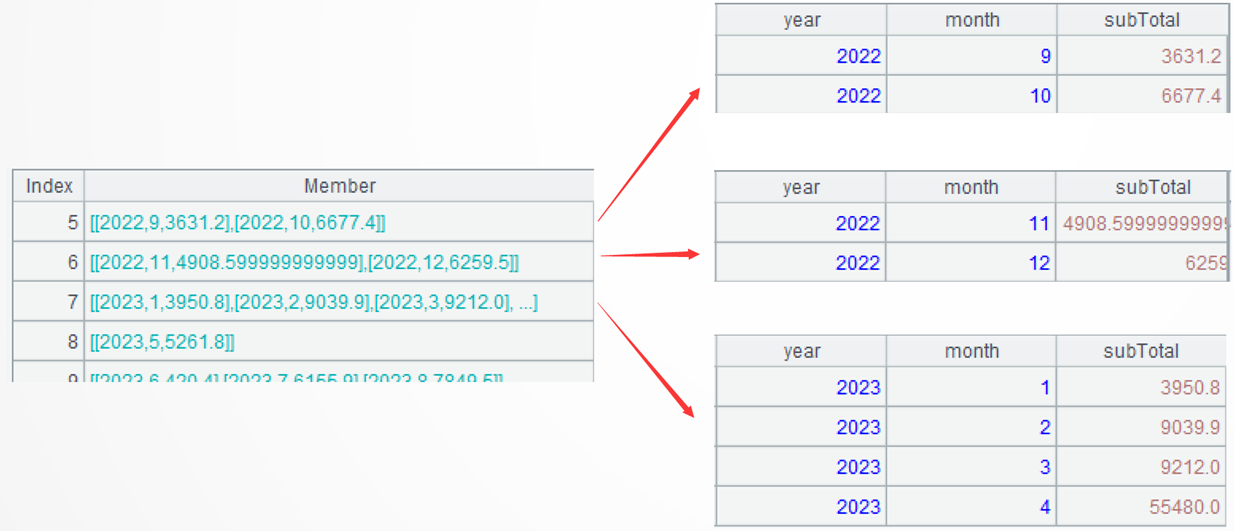
A3: Group records by bonus pool – create a new group when the cumulative value is greater than 10000 and reset the value as the current order amount. The first two groups are as follows:
A4: Create a new two-dimensional table based on A3, where each group corresponds a bonus pool and whose fields include group ID (#), 10% of the total amount in a group, list of the order numbers. The concat() function concatenates members of a sequence according to the specified separator. @c option means using comma as the separator.
Extended reading
How to retrieve the start time of the next group from the event table with esProc
From SQL to SPL: Track Production Operations Outcome Progression with Conditional NULLs
SQL, compute cumulative sums according to the termination condition
How to set duplicate content in a dataset to null with esProc
How to perform secondary grouping based on conditions within the grouped subsets with esProc
How to merge overlapping time intervals with esProc
SPL Official Website 👉 https://www.esproc.com
SPL Feedback and Help 👉 https://www.reddit.com/r/esProcSPL
SPL Learning Material 👉 https://c.esproc.com
SPL Source Code and Package 👉 https://github.com/SPLWare/esProc
Discord 👉 https://discord.gg/sxd59A8F2W
Youtube 👉 https://www.youtube.com/@esProc_SPL


