A Field Guide to Querying and Report Computations with SPL - 8 Multilevel JSON computations
8. Multilevel JSON computations
This type of tasks involves computing, generating and parsing multilevel, multidimension JSON strings. As most SQL-based systems only support a set of records of two-dimensional structure, they have to use a function to flatten the multilevel JSON to two-dimensional structure before being able to compute the data. If the JSON data has a lot of levels, the code will be very complex. Certain emerging SQL systems are indeed able to reference data at different levels, but, in the meanwhile, they also reference new methods and functions, making the code even more complex.
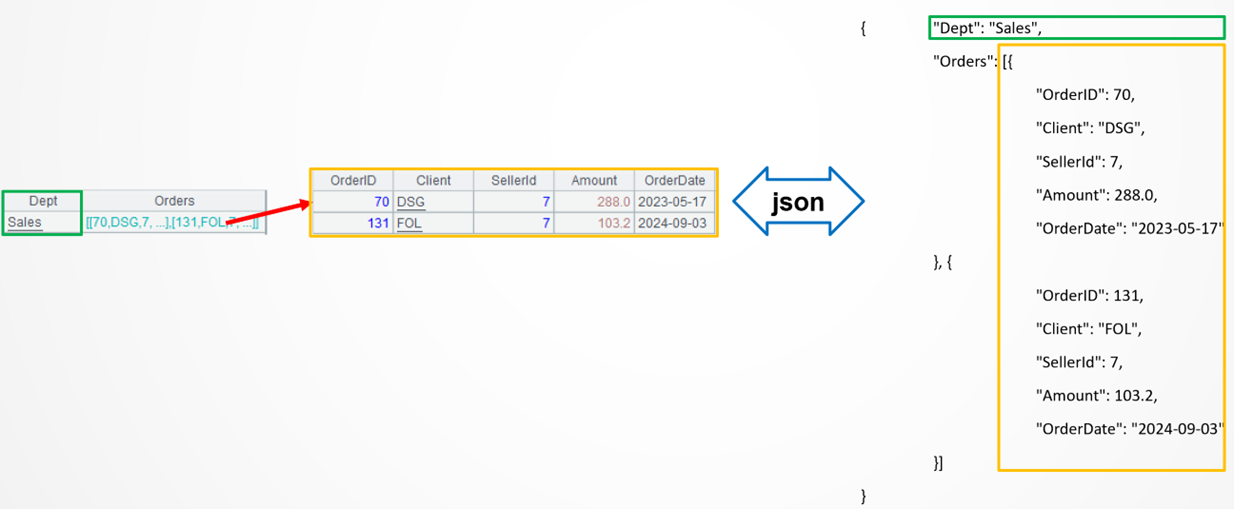
Example 1: Make the multilevel department-orders JSON data a computed column in Employee table
Source data: Employee table, Orders table
Target: Add JSON-format computed column named Sales to Employee table. The column consists of Dept object and Orders array. Dept value is obtained from Employee table, and the Order array is made up of the Orders records corresponding to employees of the current department.
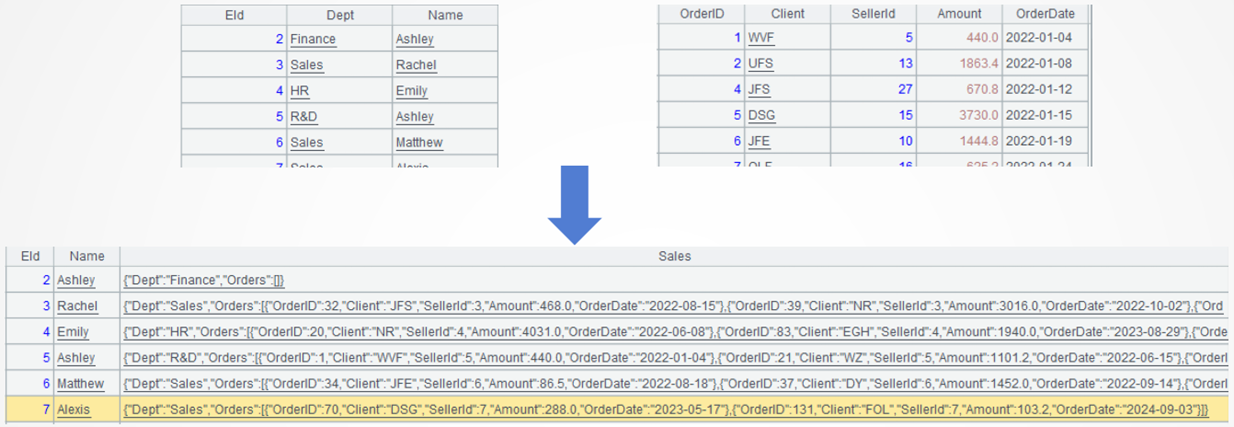
Below is the Sales field value of a record:
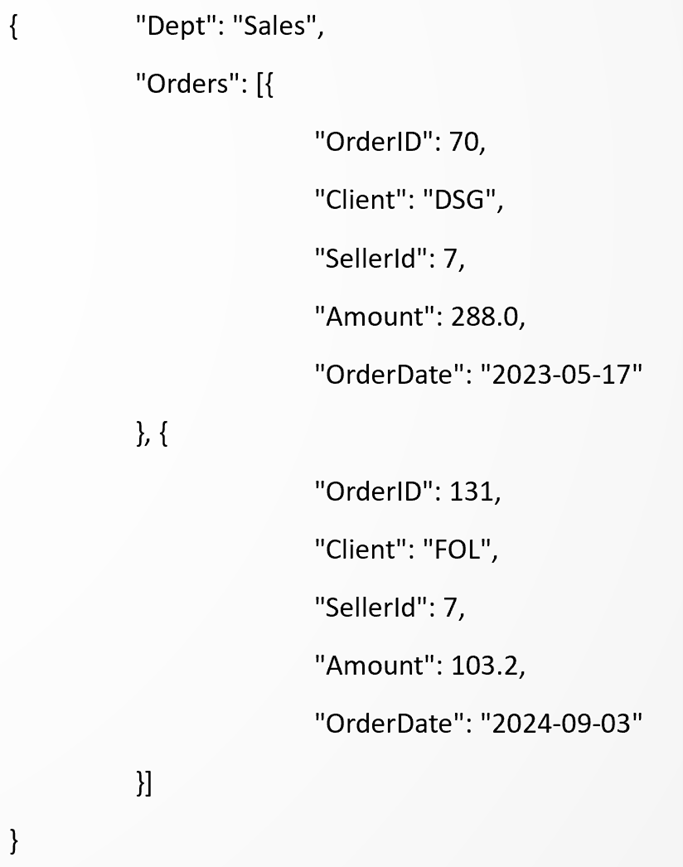
SPL code:
A |
B |
|
1 |
$select EId,Dept,Name from Employee.txt |
$select * from Orders.txt |
2 |
=A1.new(EId,Name,new(Dept,B1.select(SellerId==EId):Orders):Sales) |
|
3 |
=A2.run(Sales=json(Sales)) |
|
A1A2: Load data.
A2: Create a new table sequence based on Employee table. EId field and Name field contain simple type data and both obtain values from the original table. Sales field consists of one record of multilevel, generic structure, where Dept field has value coming from Employee table and Orders field is a set of Orders table records, which are obtained through a filtering operation. "A1.new" function creates a new table sequence based on A1’s table sequence, and "new" function creates a new record.
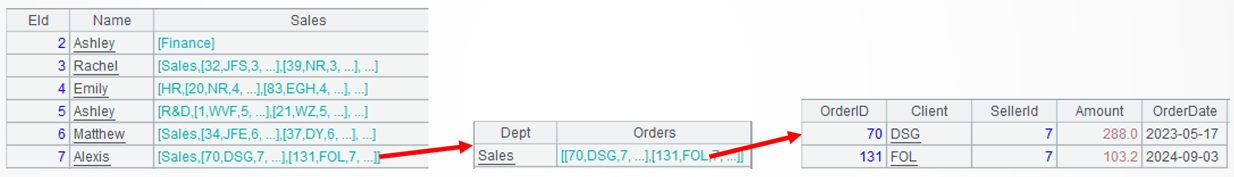
Learning point: SPL table sequences fit data of multilevel structure
Field values of a SPL table sequence are generic type, which can be simple type or array, record, set of records (table sequence) or multilevel (nested) structure, which is suitable for accommodating multilevel data.
A3: Use json() function to convert the multilevel SPL table sequence to a multilevel JSON string.
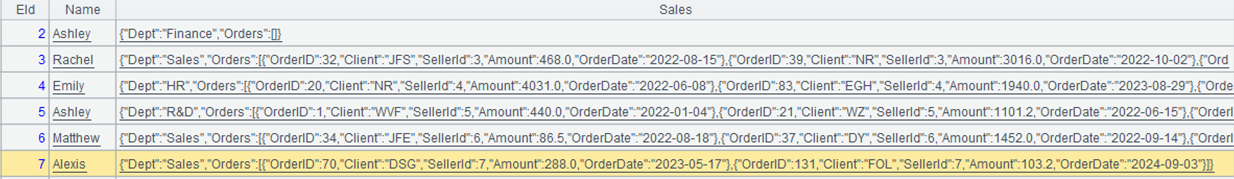
Learning point: Mutual conversion between a table sequence and a JSON string
A multilevel JSON string has two data types: object and array. Objects correspond to SPL single-field values, and arrays correspond to SPL sets of records. Each pair contains a natural correspondence relationship. SPL json() function can parse a multilevel JSON string into a multilevel table sequence, or conversely, convert a multilevel table sequence into a multilevel JSON string.
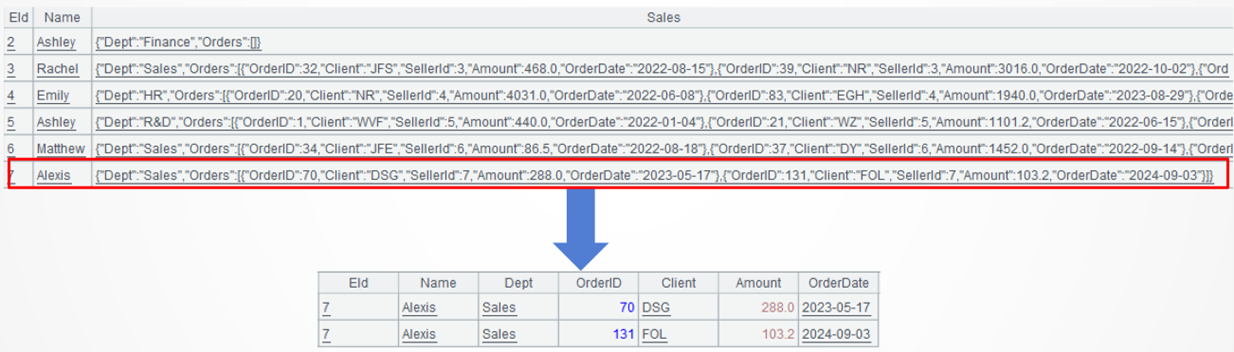
Example 2: Find specified employee records and parse their multilevel JSONS field into a two-dimensional orders table
Source data: The employee table (8/OrdersWithJsonField.txt) containing a multilevel JSON field.
Target: Find the specified employee records, and parse the multilevel JSON field named Sales by obtaining field values from level 1, level 2 and level 3 respectively and stitching them together as a two-dimensional orders table.
SPL code:
A |
|
1 |
$select * from {file("8/OrdersWithJsonField.txt").import@tf()} where EId='7' |
2 |
=A1.run(Sales=json(Sales)) |
3 |
=A2.Sales.Orders.new(A1.EId,A1.Name,A1.Sales.Dept,OrderID,Client,Amount,OrderDate) |
A1: Load data and query specified employee records. SPL automatically parses the JSON string when loading data directly from the text file rather than from the database. The import() function is used to simulate the real-world scenarios, where @f option retrieves the string, including a JSON string, without auto-parsing it.

A2: Use json() function to parse the multilevel JSON field into a SPL table sequence.

A3: Create a new two-dimensional table based on Orders field. The dot symbol is used to access the multilevel generic data to retrieve Eid field and Name field at level 1, Dept field at level 2, and OrderID, Client, Amount, OrderDate fields at level 3.
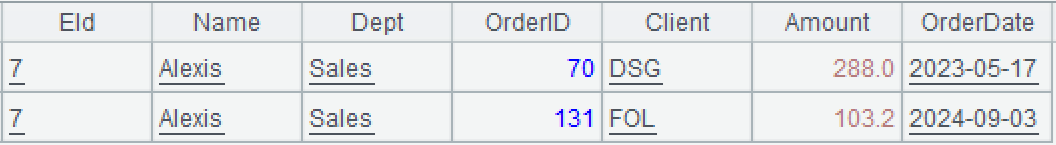
l Learning point: JSON accesses multilevel JSON data using the dot symbol (".")
The multilevel JSON data is of tree-structure. It is difficult to access a specified node using the general store formats. By parsing the multilevel JSON data into a SPL table sequence (multilevel generic type), you can use the dot symbol (".") to access a specified node. For programmers, the approach is more intuitive, is like accessing an object attribute, and is more suitable for expressing tree-structure data.
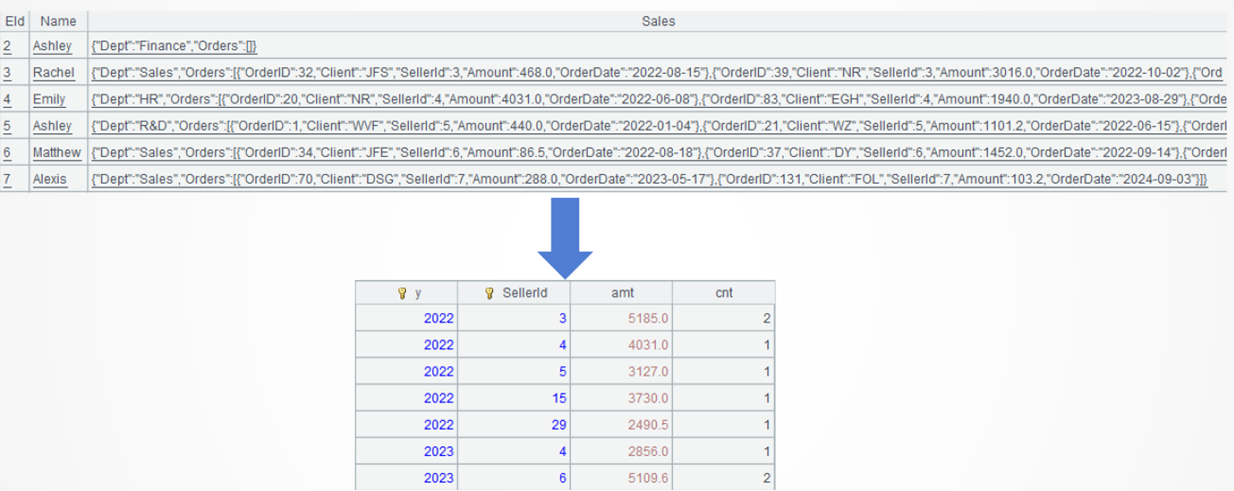
Example 3: Perform filtering to get order records at different levels of the employee table, and group and summarize them
Source data: The employee table (8/OrdersWithJsonField.txt) containing a multilevel JSON field.
Target: From the employee table find order records where the department field value at level 2 is one of the three departments ["Sales","HR","R&D"] and where the amount field value at level 3 is within the range 1000-5000, group them by year and employee, and compute total order amount and order volume in each group.
SPL code:
A |
|
1 |
$select * from 8/OrdersWithJsonField.txt |
2 |
=A1.(Sales.Orders.select( ["Sales","HR","R&D"].contain(Sales.Dept) && Amount>2000 && Amount<=5000 )) |
3 |
=A2.conj() |
4 |
=A3.groups(year(OrderDate):y,SellerId;sum(Amount):amt,count(1):cnt) |
A1: Load data, during which the JSON string of the text file will be automatically passed into a multilevel table sequence.
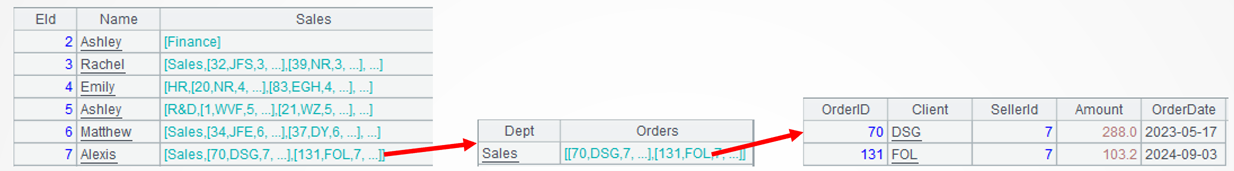
A2: Get order records where the department field value at level 2 is one of the three departments [“Sales”,“HR”,“R&D”] and where the amount field value at level 3 is within the range 1000-5000. A1.(Sales.Orders.select(…)) loops through each employee record to match the each member of the set of order records under Sales field’s Order field.
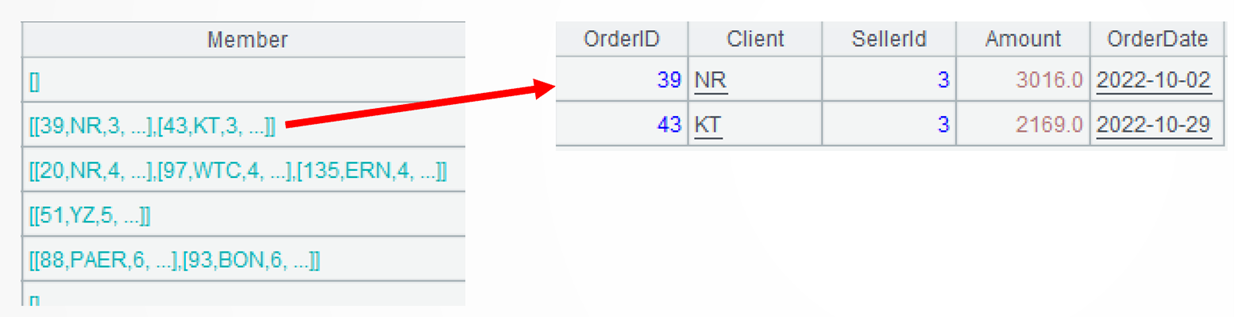
A3: Use conj()function to concatenate members from every group. A2 and A3 can be combined into one statement: A1.conj(Sales.Orders.select(…)).
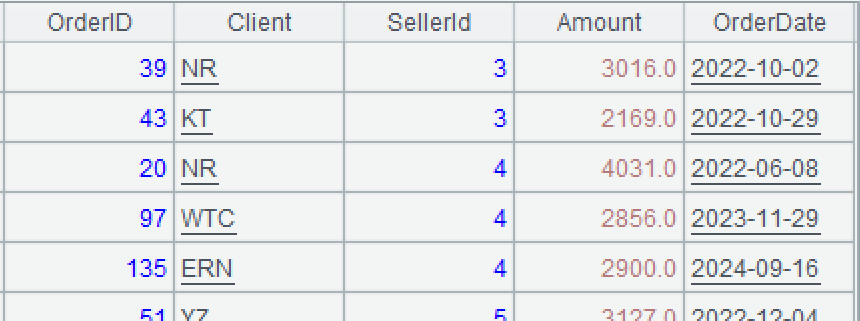
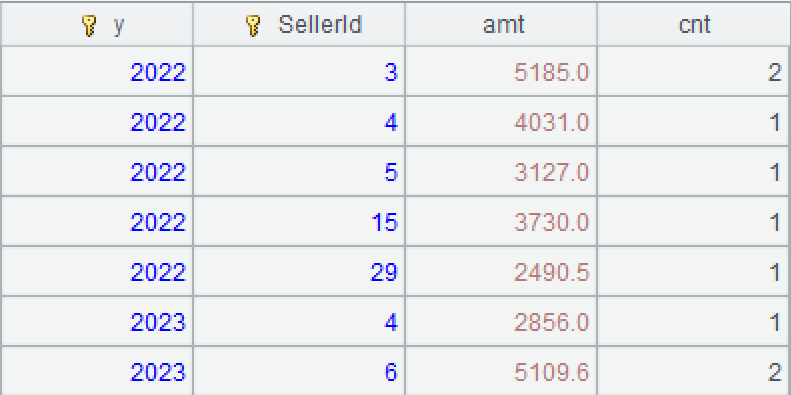
A4: Perform grouping and aggregation.
Extended reading
From SQL to SPL: Converting JSON data to Tabular in Snowflake
How to transform multi-layer sets in JSON strings with esProc
SPL: The Professional Choice for Processing Multi-Layered JSON Data
SPL Official Website 👉 https://www.esproc.com
SPL Feedback and Help 👉 https://www.reddit.com/r/esProcSPL
SPL Learning Material 👉 https://c.esproc.com
SPL Source Code and Package 👉 https://github.com/SPLWare/esProc
Discord 👉 https://discord.gg/sxd59A8F2W
Youtube 👉 https://www.youtube.com/@esProc_SPL


