A Lightweight Solution to Speed up Queries by Dumping Data to Files
Traditional transactional databases (TP) do not good at handling analytical computations. Professional OLAP databases are too heavy and often need clustering, resulting in high costs and more complicated system structure.
Storing static historical data as a lightweight esProc SPL file of columnar format enables access to SPL’s powerful computing capabilities, producing far better performance than traditional databases generate. esProc SPL is lightweight, and can run by being directly embedded in the application. It can speed up queries on dumped data while maintaining a relatively simple system structure.
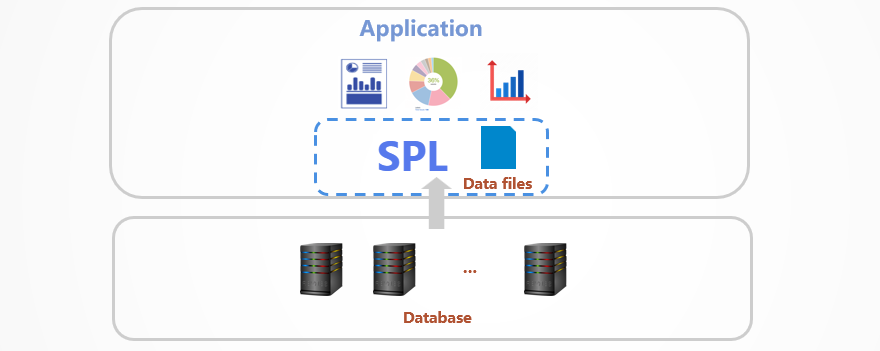
This article provides a series of practical SPL methods for speeding up external data querying:
Practice #1: Regular Filtering and Grouping & Aggregation
Practice #3: Foreign-key-based Dimension Table Join
Practice #4: Large Primary-Subtable Join
Practice #5: EXISTS at Large Primary-Subtable Join
Practice #6: Conditional Filtering by Enumerated Field
Examples in these articles cover operations having performance issues that have greatly troubled traditional databases. Those include COUNT DISTINCT, foreign-key-based JOIN, large primary-subtable JOIN (including EXISTS), conditional filtering by enumerated field (including IN), to name a few. These articles will help you break database query performance bottlenecks.
Some preparation work is required before we start.
【Here】 we have csv files and a create table SQL file to simulate part of the data of a company’s offline orders and e-commerce activities. The goal is to create tables in MYSQL database and import data from the csv files into them.

Below is the relationship between the preceding csv files:
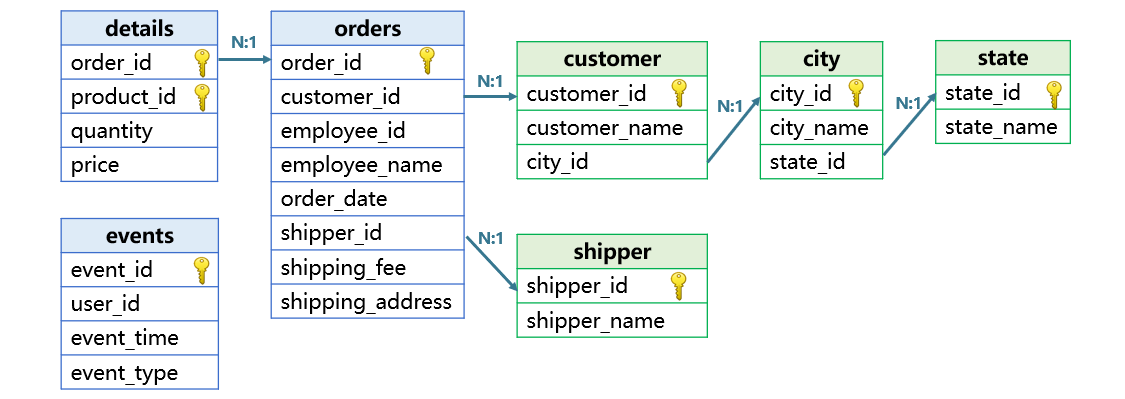
The event table (events) stores users’ actions on the e-commerce website in ten million rows and the following fields:
Fields |
Description |
Type |
Note |
event_id |
Event ID |
Integer |
Primary key |
user_id |
User ID |
Integer |
About one million IDs |
event_time |
Time when an event happens |
Datetime |
Within the year 2025 |
event_type |
Event type |
Integer |
1 represents login, 2 represents view, …, and 7 represents confirm |
Orders table (orders) stores offline orders data in ten million rows:
Fields |
Description |
Type |
Note |
order_id |
Order ID |
Integer |
Primary key |
customer_id |
Customer ID |
Integer |
|
employee_id |
Employee ID |
Integer |
|
employee_name |
Employee name |
String |
|
order_date |
Date when an order is placed |
Date |
Within the year 2024 |
shipper_id |
Shipper ID |
Integer |
|
shipping_fee |
Shipping fee |
Numeric |
|
shipping_address |
Shipping address |
String |
Orders detail (details) stores offline orders details in thirty million rows:
Fields |
Description |
Type |
Note |
order_id |
Order ID |
Integer |
Primary key |
product_id |
Product ID |
Integer |
Primary key |
quantity |
Order quantity |
Integer |
|
price |
Unit Price |
Numeric |
Customer table (customer) stores data of offline customers. The table has a relatively small amount of data:
Fields |
Description |
Type |
Note |
customer_id |
Customer ID |
Integer |
Primary key |
customer_name |
Customer name |
String |
|
city_id |
City ID |
Integer |
City table (city) stores data of cities where offline customers are based. The table has a relatively small amount of data:
Fields |
Description |
Type |
Note |
city_id |
City ID |
Integer |
Primary key |
city_name |
City name |
String |
|
state_id |
State ID |
Integer |
State table (state) stores data of states where offline customers come from. The table has a relatively small amount of data:
Fields |
Description |
Type |
Note |
state_id |
State ID |
Integer |
Primary key |
state_name |
State name |
String |
Shipper table (shipper) stores data of offline shippers. The table has a relatively small amount of data:
Fields |
Description |
Type |
Note |
shipper_id |
Shipper ID |
Integer |
Primary key |
shipper_name |
Shipper name |
String |
Download esProc. The Standard Edition is enough.
After installing esProc, check whether a database can be successfully accessed from IDE. Take MYSQL as an example. Put the database’s JDBC in "[installation directory]\common\jdbc", which is one of esProc’s classpaths:

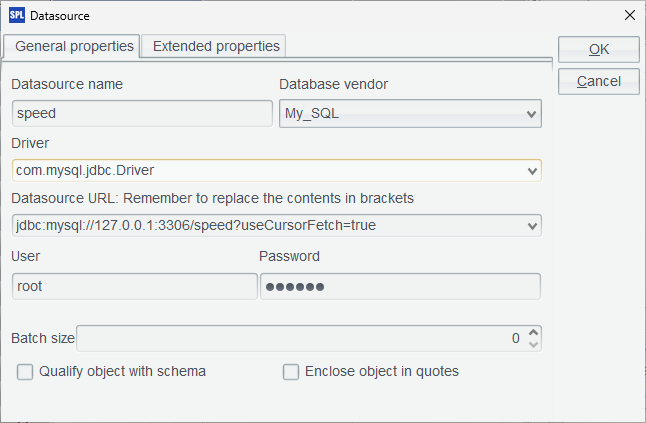
To create MYSQL data source in esProc, select Tool ->Connect to Data Source on the menu, configure the standard MySQL JDBC connection named speed:
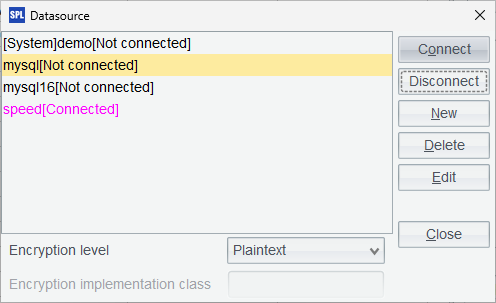
Return to the Datasoure window and connect to the configured data source just now. The setup is successful if the data source name turns pink.
Create a new script in IDE, write SPL statements, and connect to the database to load data from orders table through an SQL statement.
SPL code example 1:
A |
|
1 |
=connect("speed") |
2 |
=A1.query@x("select * from orders limit 100") |
Press Ctrl-F9 or click the Execute button and then click A2, and there are 100 records listed to the right.
The SPL code is written in the grid, where a cell name can be directly used as a temporary variable.
Look up Tutorial and Function Reference if you have any problems.
The environment where our tests are performed comprises VMware virtual machine, 8-core CPU, 8G RAM, SSD drive, Windows 11 OS, MySQL 8.0, and esProc SPL Standard Edition.
SPL Official Website 👉 https://www.esproc.com
SPL Feedback and Help 👉 https://www.reddit.com/r/esProcSPL
SPL Learning Material 👉 https://c.esproc.com
SPL Source Code and Package 👉 https://github.com/SPLWare/esProc
Discord 👉 https://discord.gg/sxd59A8F2W
Youtube 👉 https://www.youtube.com/@esProc_SPL



Chinese version