A Field Guide to Querying and Report Computations with SPL - Preparation
Preparation
Download and install esProc. The Standard Edition is recommended.
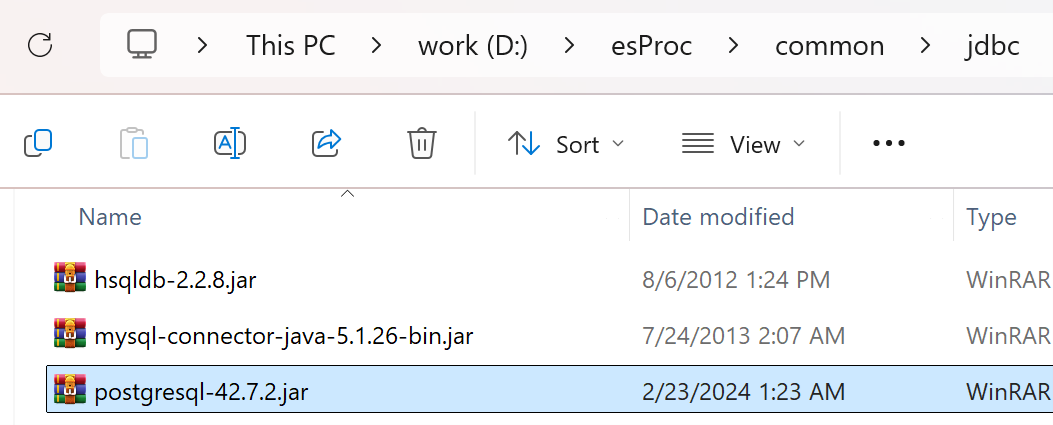
After installing esProc, check if the esProc IDE can access the database normally. First, place the database’s JDBC driver in the directory [installation directory]\common\jdbc, which is one of esProc’s classpaths. Below is PostgreSQL’s JDBC:
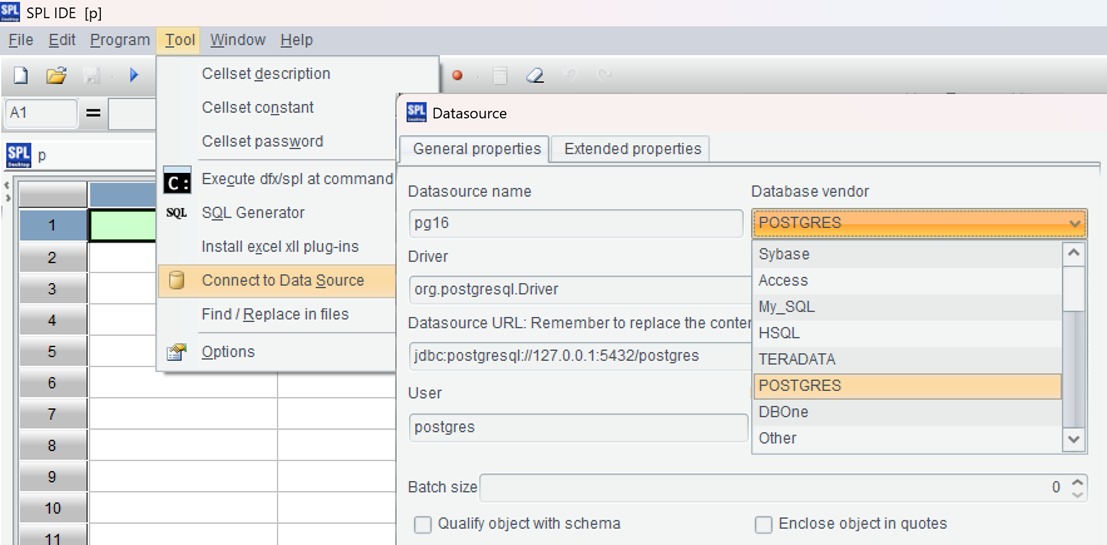
Open esProc IDE, navigate to the menu “Tool -> Connect to Data Source” to create a new JDBC data source, and fill in the connection details for the specific database. Note that the data source name will be used in future code.
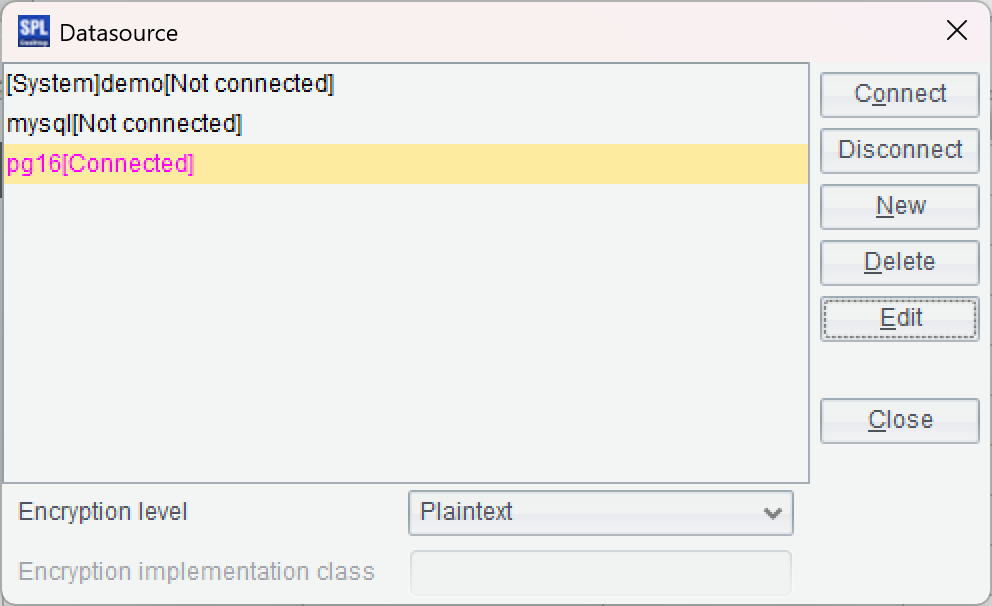
Return to the data source interface and connect to the data source you just configured. If the data source name turns pink, it means the configuration was successful.
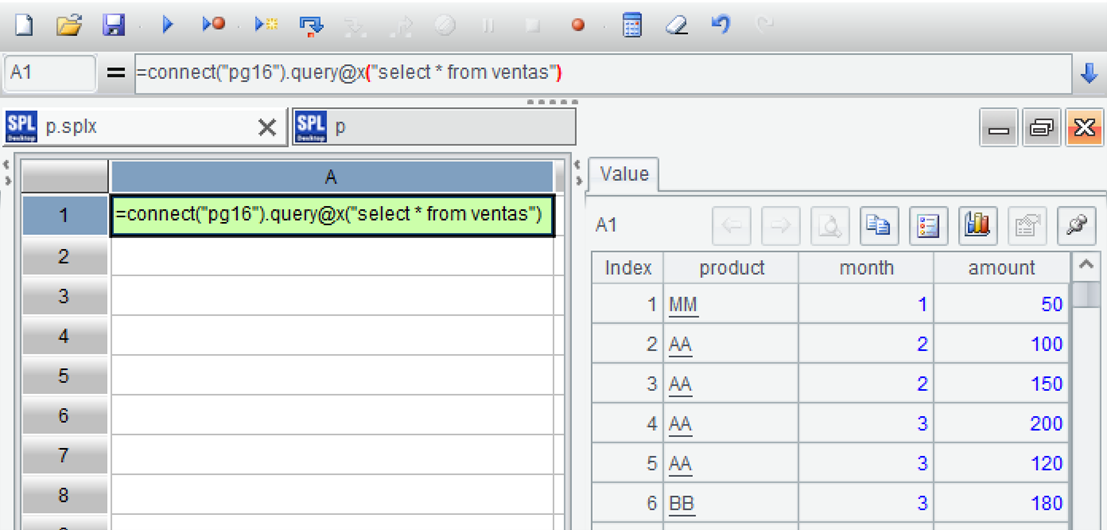
In the IDE, create a new script and write SPL statements to connect to the PostgreSQL database, loading data through simple SQL:
=connect("pg16").query@x("select * from ventas")
Press Ctrl+F9 to execute, and you can see the results, displayed in a table format, on the right part of the IDE. This is convenient for debugging the SPL code.
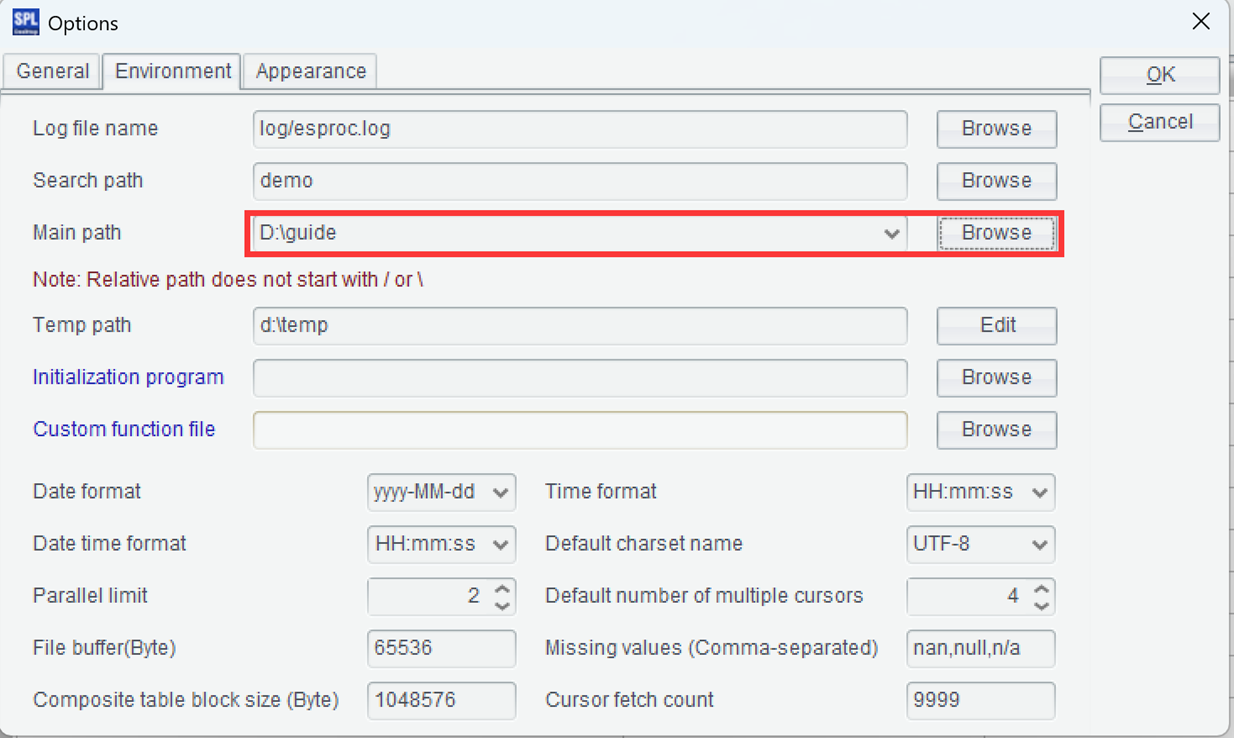
Next, let’s try using the public datasets mentioned above. First, set the “Main path” in the configuration options to point to the root directory where the public datasets are located.
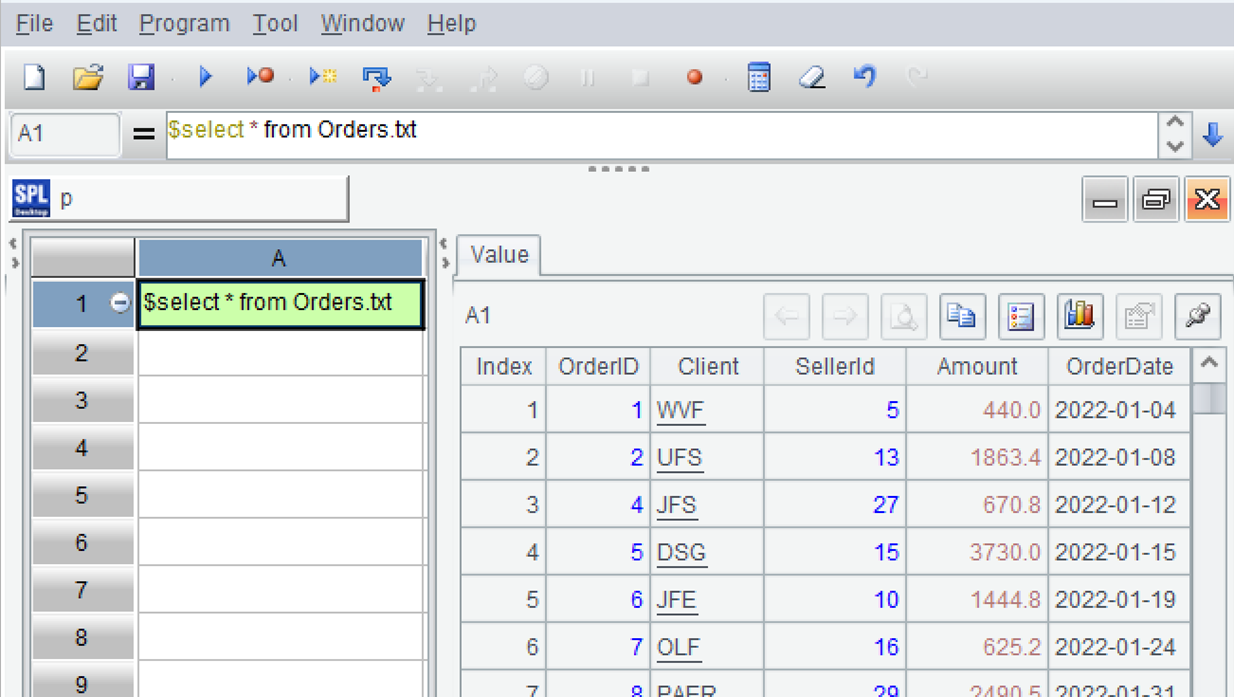
Then write a simple SQL statement to load the text file, execute the SQL, and observe the result.
Perform debugging in the IDE, and then proceed to configure the Java application environment.
Find esProc JDBC-related jar files, esproc-bin-xxxx.jar and icu4j_60.3.jar, in [installation directory]\esProc\lib:
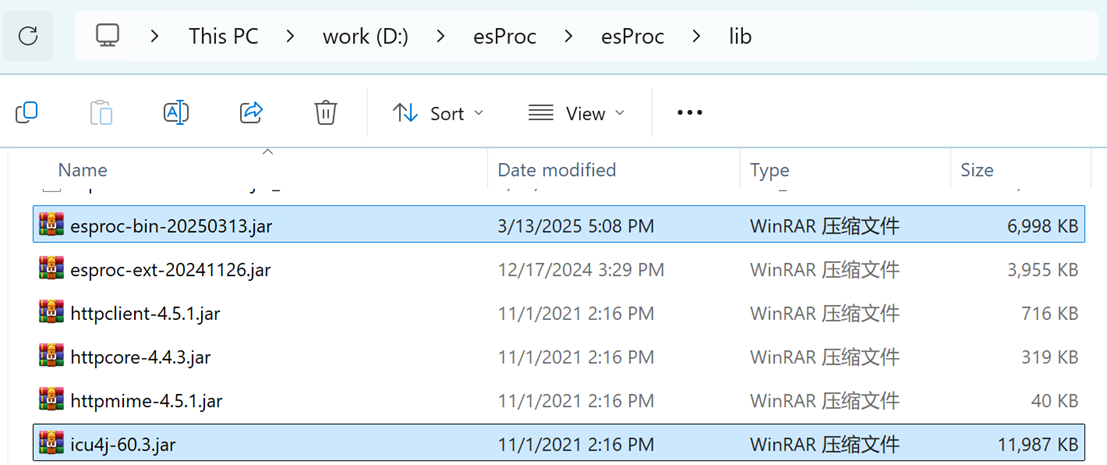
Deploy those two jar files to the classpath of the Java development environment.
Locate esProc configuration file raqsoftConfig.xml in directory [installation directory]\esProc\config, and also deploy it to the classpath of the Java development environment.
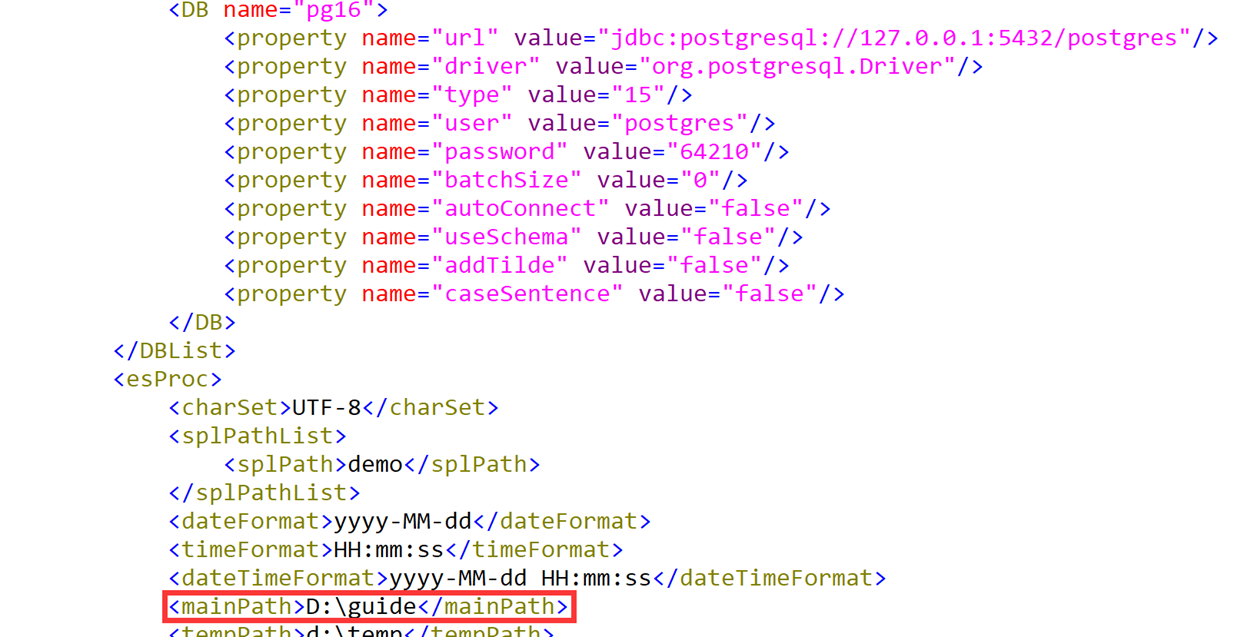
The item to check in the configuration file is mainPath, which represents the default path for a script file or any of the other files. Note that the data source information is also stored in the configuration file.
Now you can write Java code and execute the SPL code through esProc JDBC.
A relatively short piece of SPL code can be directly embedded into the Java application, which is similar to the embedment of SQL code in the Java application.
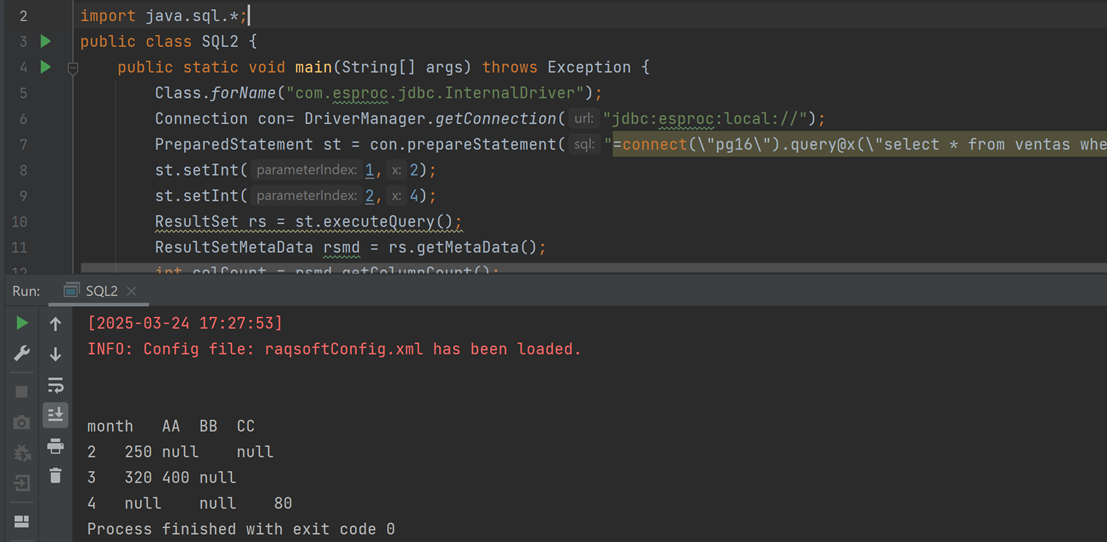
PreparedStatement st = con.prepareStatement("=connect(\"pg16\").query@x(\"select * from ventas where month>=? and month<=?\",?,?).pivot@s(month;product,sum(amount))");
st.setInt(1,2);
st.setInt(2,4);
ResultSet rs = st.executeQuery();
Execute the SPL code and you get result as shown below:
Longer SPL code can be saved as a script file. esProc JDBC calls SPL code through the file name, a process similar to how JDBC calls the database stored procedure, which will not be elaborated further here.
SPL Official Website 👉 https://www.esproc.com
SPL Feedback and Help 👉 https://www.reddit.com/r/esProcSPL
SPL Learning Material 👉 https://c.esproc.com
SPL Source Code and Package 👉 https://github.com/SPLWare/esProc
Discord 👉 https://discord.gg/sxd59A8F2W
Youtube 👉 https://www.youtube.com/@esProc_SPL


