7.3 Prediction
Having obtained the initial cluster centroids, passing them to the k-means algorithm allows us to obtain the centroids corresponding to each production route. When new yield data, Y, needs to be assigned a cluster (production route), we simply identify the nearest centroid for each member in Y, thus assigning that member to the corresponding cluster.
The process is as follows:
Prediction data Y:
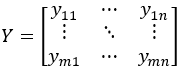
Where each row of Y represents the yields of the various outputs for a given day’s production data. These rows can be viewed as points in a high-dimensional space. To classify each point, we calculate its distance to all centroids; the point is then assigned to the cluster associated with the nearest centroid.
Training data cluster centroid, C:
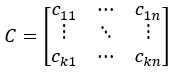
Cluster assignments for data points in Y, Yc:
yci=t,t=pmin(dis(Yi,Ct))
Where yci represents the cluster label assigned to the i-th data point Yi in Y, and Ct is the centroid of the t-th cluster.
SPL routine:
| A | B | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | [[0.116,0.371,0.307], [0.143,0.324,0.303]] |
/Y |
| 2 | [[0.117,0.339,0.315], [0.179,0.257,0.332], [0.139,0.254,0.371]] |
/C |
| 3 | =A1.((y=~,A2.pmin(dis(~,y)))) | /Yc |
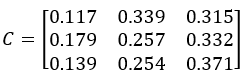
Calculation result example:
Predicted data Y:

Centroid C:
Cluster assignments for members in Y, Yc:
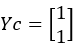
SPL Official Website 👉 https://www.esproc.com
SPL Feedback and Help 👉 https://www.reddit.com/r/esProcSPL
SPL Learning Material 👉 https://c.esproc.com
SPL Source Code and Package 👉 https://github.com/SPLWare/esProc
Discord 👉 https://discord.gg/sxd59A8F2W
Youtube 👉 https://www.youtube.com/@esProc_SPL


