A Field Guide to Querying and Report Computations with SPL - 11 Datetime sequence computations
This type of task refers to computations involving ordered sets whose members are datetime. In addition to common challenges such as order-based computations, SQL is also inconvenient for generating datetime sequences. It often requires helper tables or recursive statements, resulting in complex code structures and tedious code.
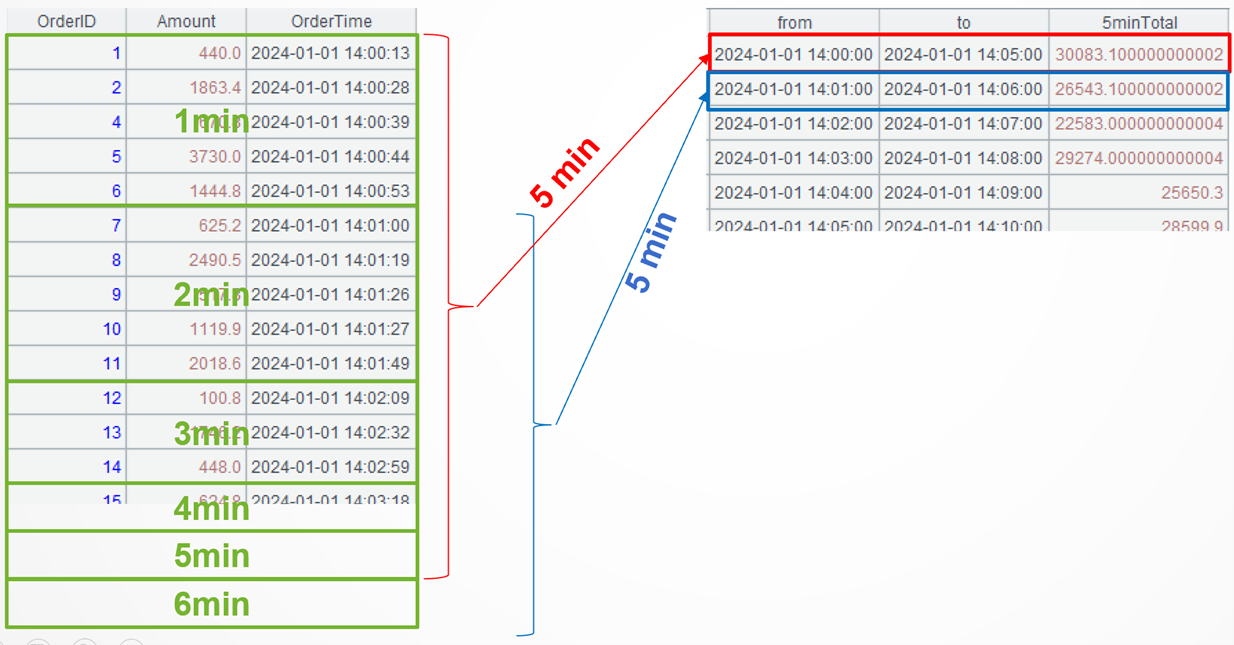
Example 1: Perform aggregation every minute on online orders table records generated within a 5-minute time window
Source data: Multiple order records per minute are generated for online orders table (11/Orders_online.txt).
Target: Sum order amounts every minute. Each aggregation covers records generated within a 5-minute time window – specifically, orders placed from the current minute through the fourth minute following it.
SPL code:
A |
|
1 |
$select * from 11/Orders_online.txt |
2 |
=A1.groups(datetime@m(OrderTime):min;sum(Amount):minTotal) |
3 |
=A2.new(min:from, elapse@s(from,300):to, minTotal[0:4].sum(): 5minTotal) |
4 |
=A3.m(:-5) |
A1: Load data.
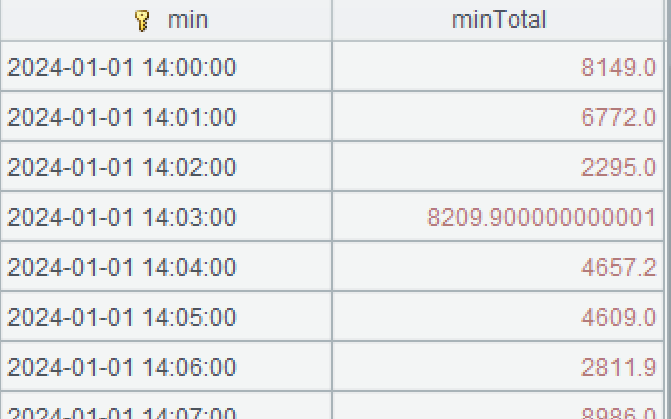
A2: Perform grouping and aggregation on order records by minute. The datetime() function adjusts the time precision. @m option enables accuracy to the minute – get the minute of the time.
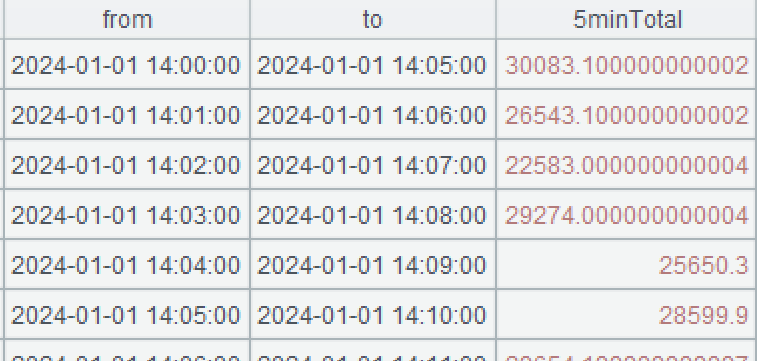
A3: Generate a new two-dimensional table based on A2 by aggregating records (per minute) at 300 second (5 minute) interval. “from” is taken as the time of the current record; “to” is taken as the time 5 minutes after the current record; and “payload” is the aggregate during the interval from the current record to the fourth record after it. The elapse()function computes a new time after adding or subtracting a time duration. The default unit is the day. @s option indicates that the unit is second. The notation [0:4] is SPL’s syntax for representing a relative range.
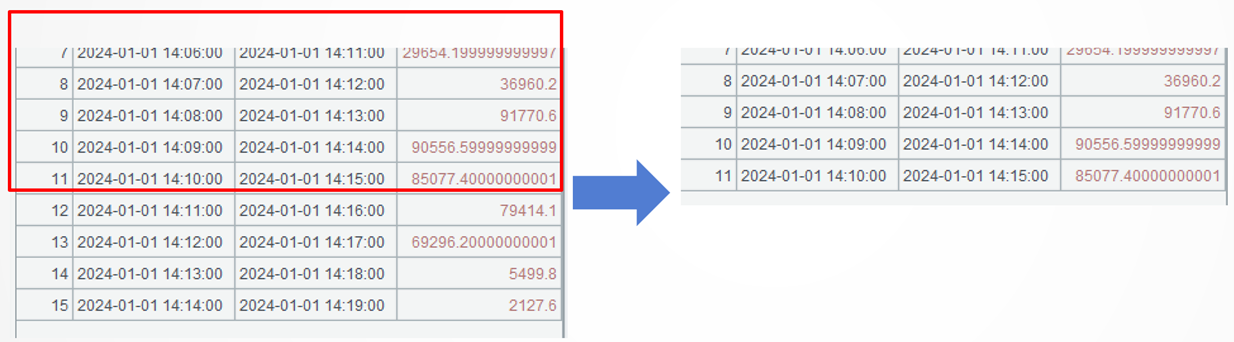
A4: The last 4 records of A3’s result set are meaningless, so we just retrieve records from the first to the 5th to last. The m() function gets members according to their absolute positions.
Example 2: Merge overlapping date ranges in customer after-sales service
Source data: In after-sales service table (11/after_sales_service.txt), each customer can have multiple after-sales service periods active at the same time, and these periods may overlap.
Target: Merge the overlapping service periods for each client.
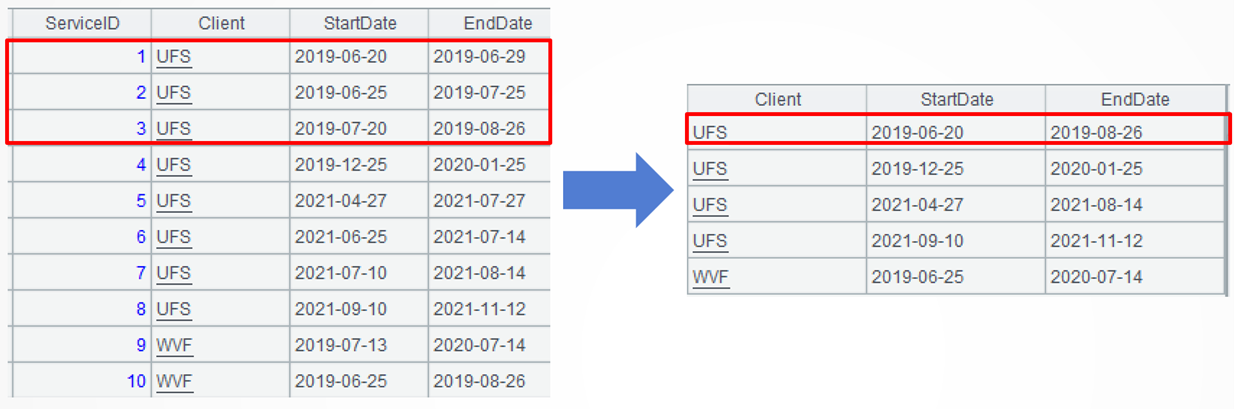
SPL code:
A |
|
1 |
$select * from 11/after_sales_service.txt |
2 |
=A1.group(Client) |
3 |
=A2.(~.(periods(StartDate,EndDate)).merge@u() .group@i(~!=~[-1]+1).new(A2.Client,~1:StartDate,~.m(-1):EndDate)) |
4 |
=A3.conj() |
A1: Load data.
A2: Group records by client without aggregation. Each group consists of one set. Below is the first group:
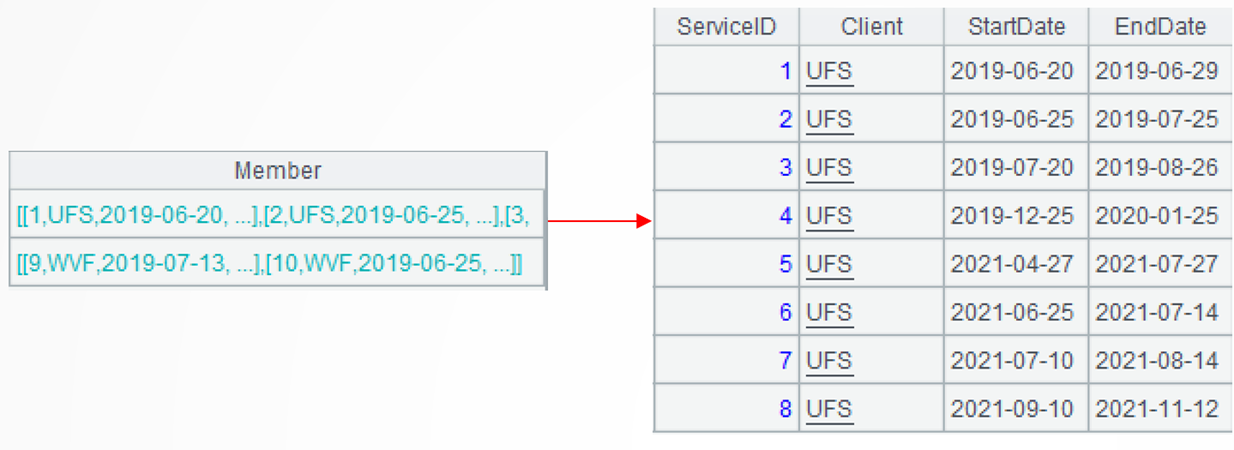
A3: =A2.(~.(periods(StartDate,EndDate))) process each group of data in A2 in several steps. First, loop through each record of the current group and generate a date sequence according to the starting date and the ending date. Below is the first date sequence of the first group:
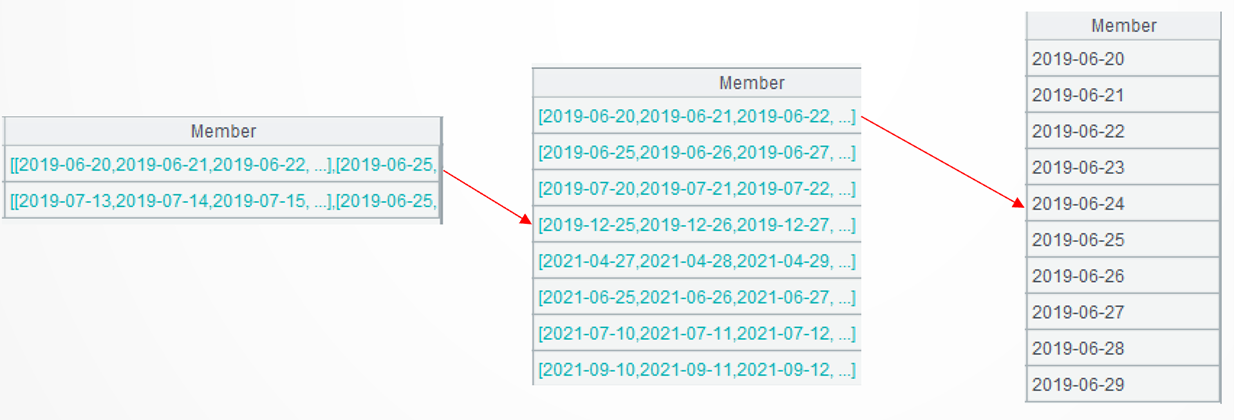
.merge@u()furthers the computation to perform union on sequences of the current group and generate distinct date sequences. The merge() function merges members of an ordered set. @u option enables a union operation at merge. Here are the first two date sequences in the first group:
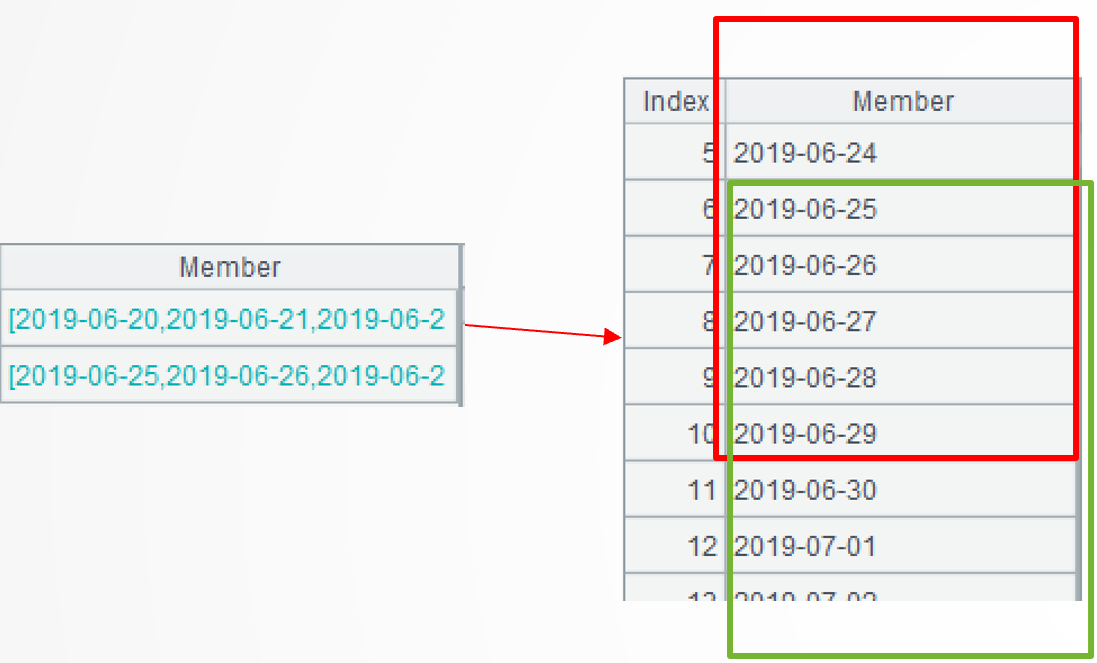
group@i(!=[-1]+1) continues the computation. It groups records of each sub-sequence without aggregation by putting continuous dates in the same subgroup. The group@i function performs conditional grouping on an ordered set. !=[-1]+1 means creating a new group when the current member is unequal to the preceding member plus 1. Here are the first two subgroups in the first group:
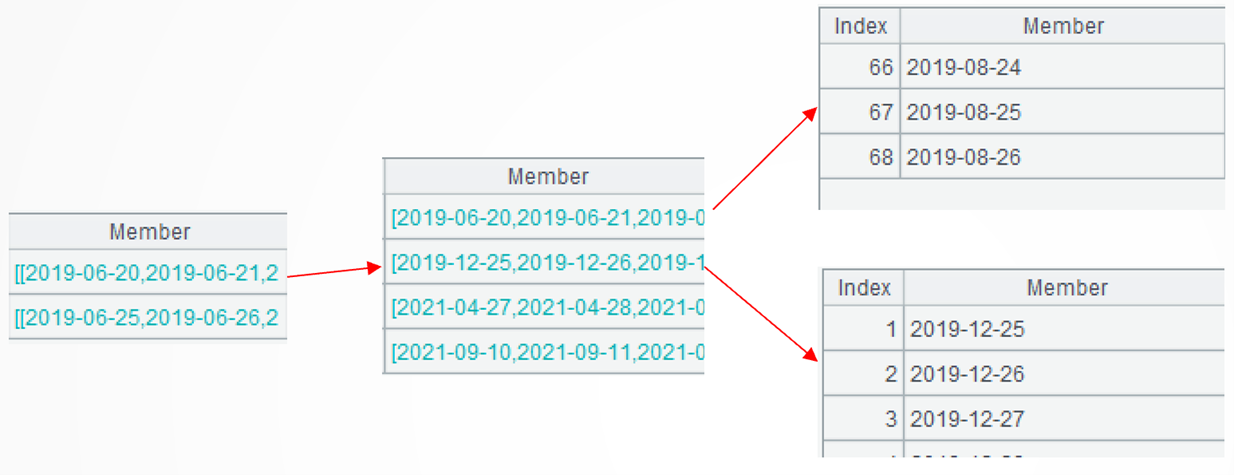
.new(A2.Client,1:StartDate,.m(-1):EndDate) performs the computation further to generate a two-dimensional table based on the current group. Each subgroup generates one record, where the starting date gets from the subgroup’s first member and the ending date gets from the last member of the subgroup.
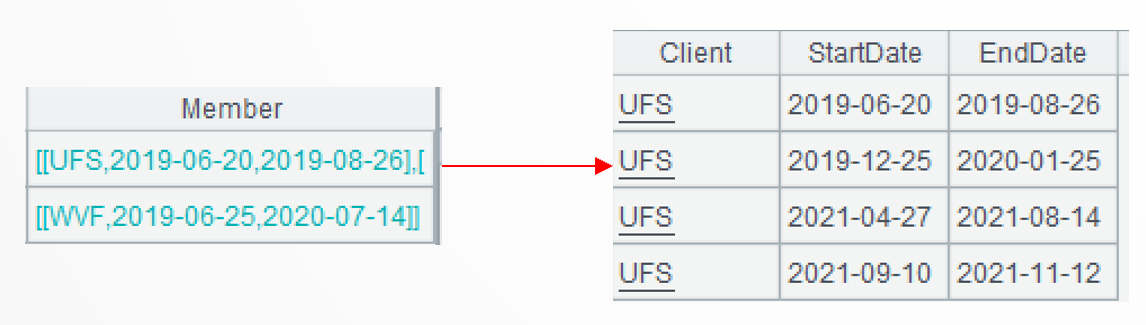
A3: Concatenate members of all subgroups.
Example 3: Compute the monthly balance for each account and fill in any missing months
Source data: Account transaction history table (11\transactions.txt) stores the debit and credit transaction records for multiple accounts, with non-consecutive dates.
Target: Compute the monthly balance for each account from the beginning (2021-01) to the end of the period (2024-04) while filling in the missing months.
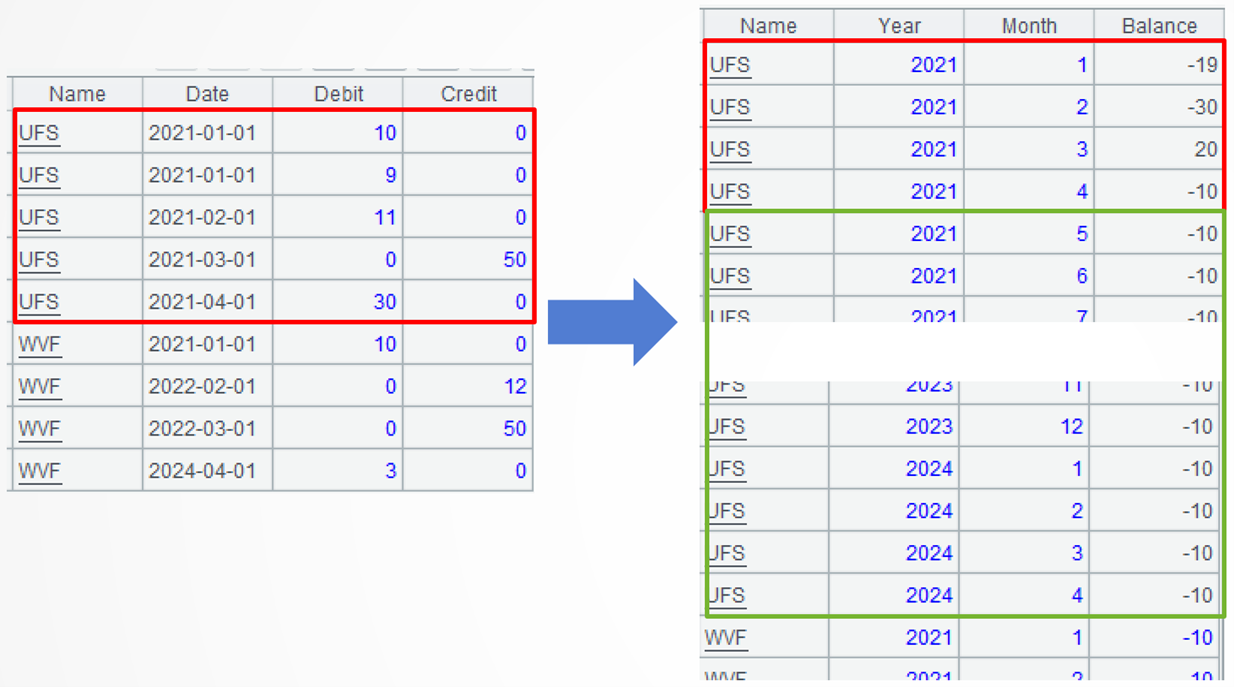
SPL code:
A |
|
1 |
$select Name,YM,sum(Credit - Debit) as Change from(select Name, date(NUMTOCHAR(year(Date))+'-'+NUMTOCHAR(month(Date))+'-01')as ym,Credit,Debit from 11\transactions.txt) group by Name,ym |
2 |
=periods@m(date("2021-01-01"),date("2024-04-01"),1) |
3 |
=xjoin(A1.id(Name):Name; A2:YM) |
4 |
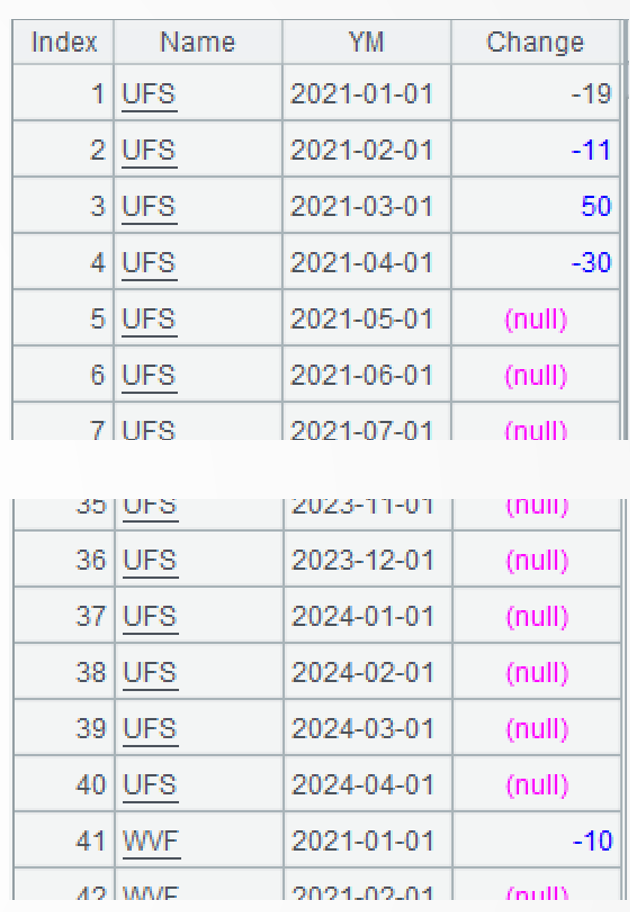
=A3.join(Name:YM, A1:Name:YM,Change) |
5 |
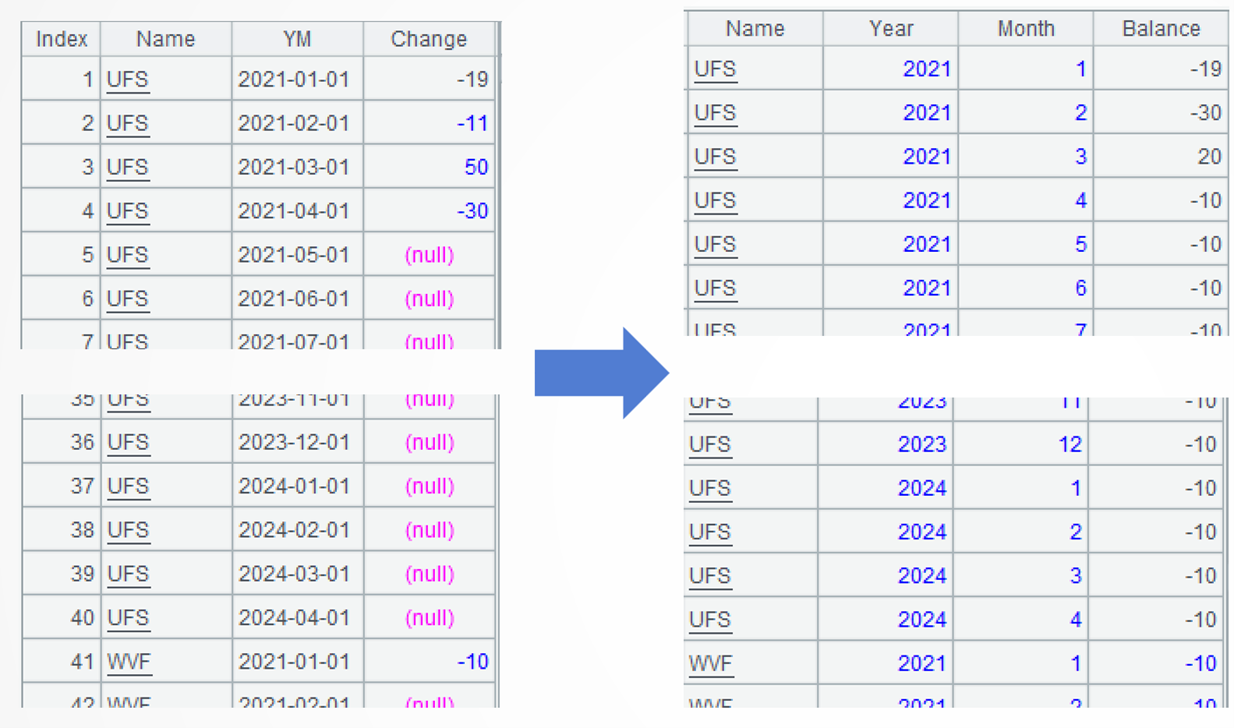
=A4.new(Name,year(YM):Year,month(YM):Month,Change+if(Name==Name[-1] , Balance[-1]):Balance) |
A1: Load data: group records by account and the first day of each month and compute the monthly amount change (debit - credit).
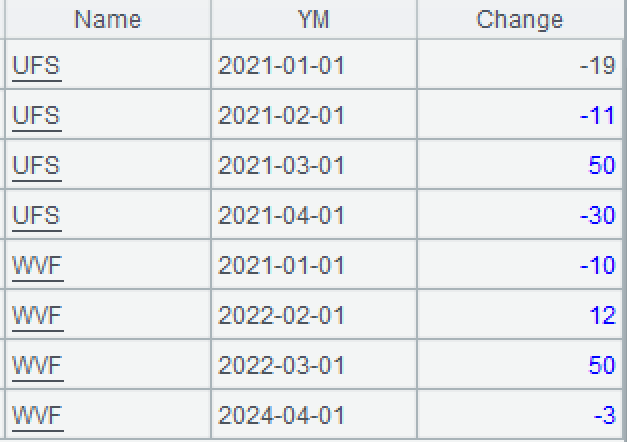
A2: Generate a sequence of months represented by the first month days according to the beginning and ending of the period. The periods() function generates a date sequence. @m option enables using month as the unit of time interval.
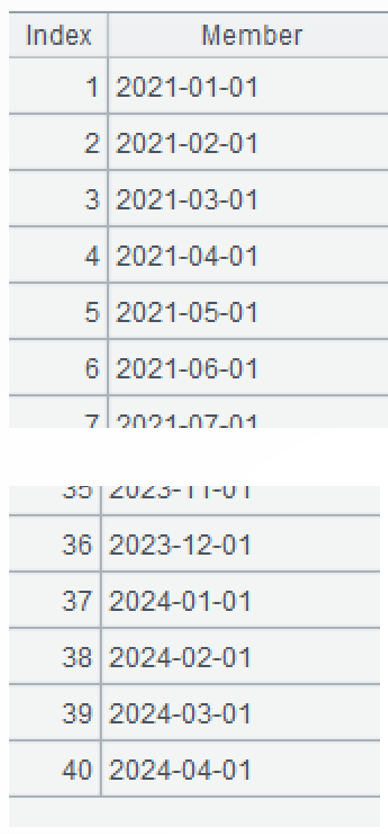
A3: Compute the cross join of the account sequence and the month sequence. The xjoin() function performs cross join operation.
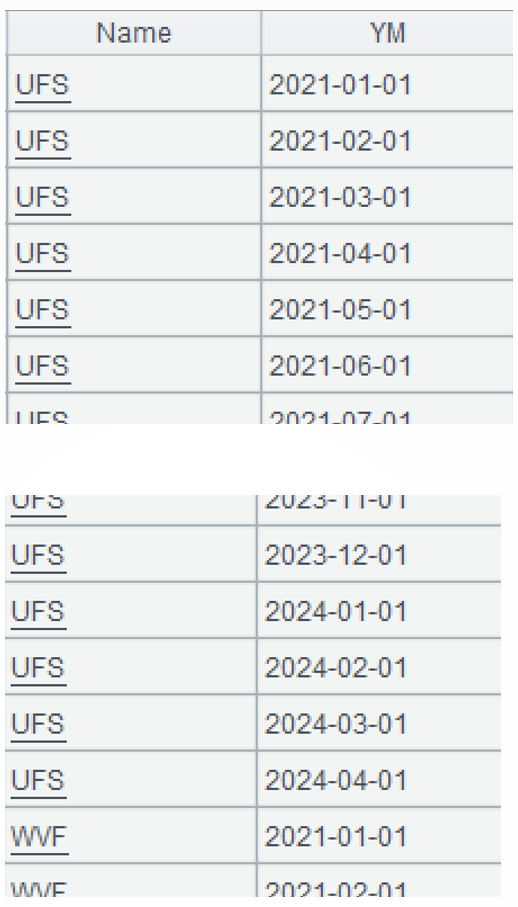
A4: Perform left join between A3 (the cross join of account sequence and month sequence) and A1(each account’s monthly amount change).
A5: Transform the date field into year field and month field, and use relative position syntax to accumulate the monthly balance for each account.
When the current account remains the same as the previous record, the monthly balance equals the current month’s amount change plus the previous month’s balance.
When the account changes, the monthly balance is initialized to the current month’s amount change.
Extended reading
From SQL to SPL: Aggregate according to time interval
How to merge overlapping time intervals with esProc
From SQL to SPL: Count date ranges per year
From SQL to SPL: Calculate monthly account balance and fill in missing dates
SPL Official Website 👉 https://www.esproc.com
SPL Feedback and Help 👉 https://www.reddit.com/r/esProcSPL
SPL Learning Material 👉 https://c.esproc.com
SPL Source Code and Package 👉 https://github.com/SPLWare/esProc
Discord 👉 https://discord.gg/sxd59A8F2W
Youtube 👉 https://www.youtube.com/@esProc_SPL


